Data extraction involves scraping techniques to gather data from various sources. Two primary methods for extracting data include web scraping and screen scraping.
Even though web scraping and screen scraping share some similarities, they are fundamentally different in their approaches and applications.
This blog explains in detail the concept, use cases, and challenges of web scraping and screen scraping and their relationship with robotic process automation (RPA).
1. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: The Concept
What is Web Scraping?
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites using automated scripts or bots that navigate web pages, retrieve HTML content, and parse it.
Through web scraping, you can target any data available on the web, like text, images, links, etc.
It is used for various purposes, including market research, price comparison, content aggregation, and competitive analysis.
What is Screen Scraping?
Screen scraping is extracting data from the display output of an application. It mimics human interaction with the computer screen, capturing pixel data and converting it into structured information.
Screen scraping is also used to extract data from legacy systems, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), and other applications where direct access to the data is impossible.
2. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: Methods
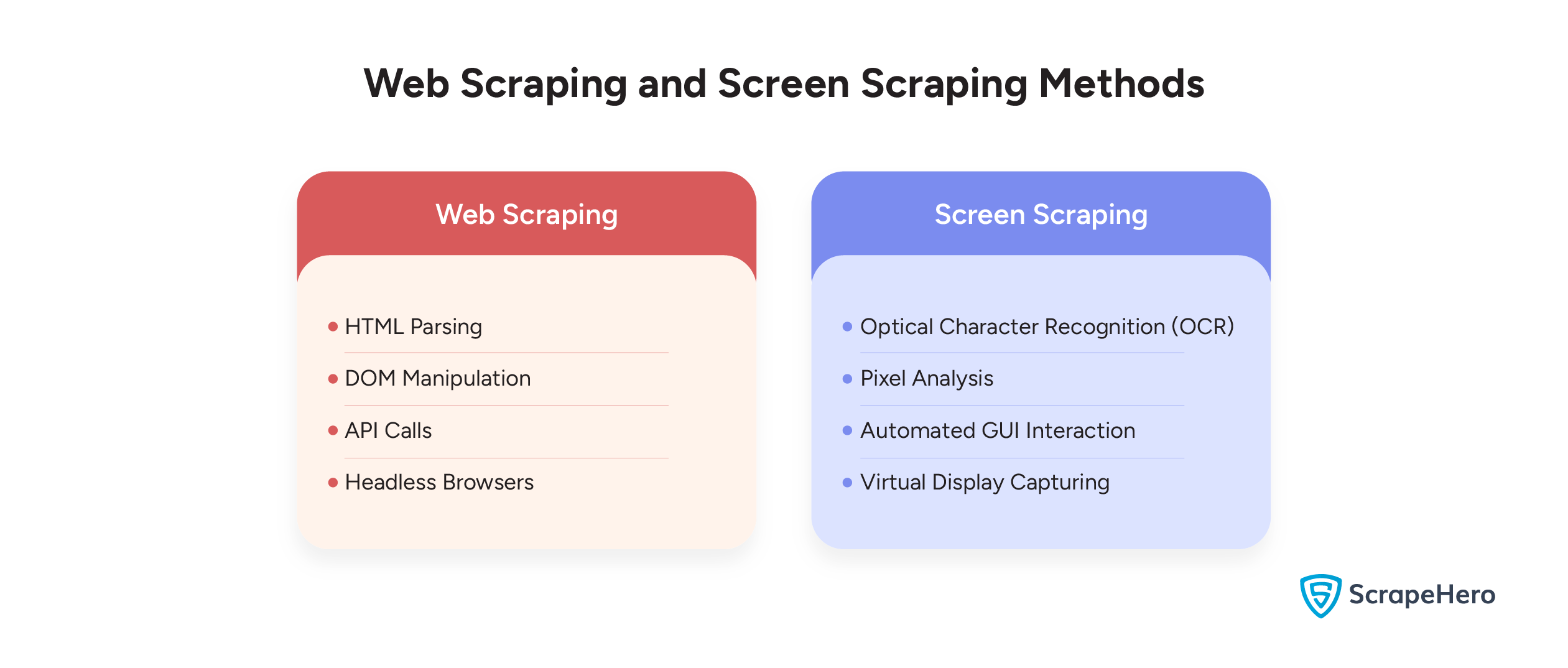
Web Scraping Methods
Various methods by which you can extract data through web scraping include:
- HTML Parsing
- DOM Manipulation
- API Calls
- Headless Browsers
-
HTML Parsing
HTML Parsing is the process of analyzing web page HTML code using libraries such as BeautifulSoup, lxml, or Cheerio and extracting relevant data. -
DOM Manipulation
To extract dynamic content, you may have to navigate and manipulate the Document Object Model (DOM) using tools like Selenium or Puppeteer.
-
API Calls
Data is also accessed through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) provided by websites. API calls are the medium by which APIs interact.
-
Headless Browsers
Using headless browsers like PhantomJS or headless Chrome, you can scrape data from web pages without rendering the user interface.
Screen Scraping Methods
Various methods by which you can extract data through screen scraping include:
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
- Pixel Analysis
- Automated GUI Interaction
- Virtual Display Capturing
-
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Using OCR technology, you can convert images of text into machine-readable text.
-
Pixel Analysis
To identify and extract information from the screen, you need to capture and analyze pixel data.
-
Automated GUI Interaction
To automate interactions with graphical user interfaces and capture data, you can use tools like Selenium, AutoIt, or Sikuli.
-
Virtual Display Capturing
You can also capture screen output without interfering with the actual user interface by creating virtual displays.
3. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: Working
How Web Scraping Works
Here’s the step-by-step process involved in web scraping:
- Identify Target Website
- Send HTTP Requests
- Parse HTML Content
- Handle Dynamic Content
- Extract Information
- Store and Use Data
-
Identify Target Website
You need to determine the website and specific pages that you need to scrape before beginning the process.
-
Send HTTP Requests
The next step is to retrieve the HTML content. To do this, you need to use scripts or tools to send HTTP requests to the target website.
-
Parse HTML Content
To extract the desired information, you need to parse the HTML content using various Python libraries or frameworks.
-
Handle Dynamic Content
At times, there may be situations where the web pages are JavaScript loaded. To handle such dynamic content, tools like Selenium or Puppeteer are used.
-
Extract Information
Next comes the data extraction. Relevant data, such as text, images, or links, are extracted from the parsed HTML.
-
Store and Use Data
It is essential to store the extracted data in a structured format, such as a database or CSV file, for further use or analysis.
How Screen Scraping Works
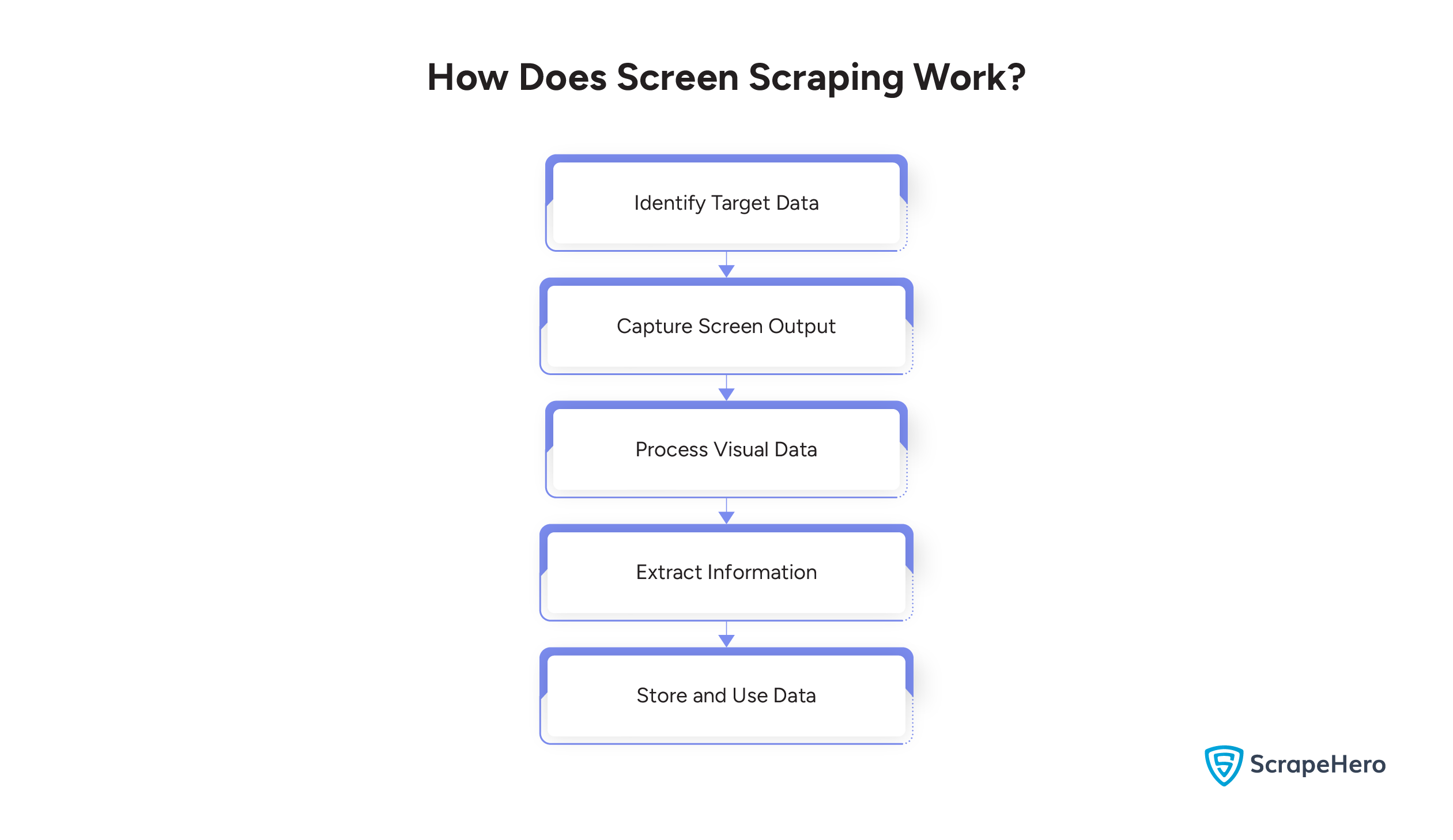
Here’s the step-by-step process of how screen scraping works:
-
Identify Target Data
First, determine the specific data that you need to extract from the screen.
-
Capture Screen Output
Your data may include text, images, or other visual elements. To capture the screen output effectively and handle diverse data types, you can use specialized tools or scripts.
-
Process Visual Data
To convert visual data into machine-readable text or structured data, you have to apply techniques such as OCR.
-
Extract Information
Now, from the processed data, you can parse and extract the relevant information.
-
Store and Use Data
Storing the extracted data in a structured format, such as a database or spreadsheet, is the final step.It ensures that your data is organized and ready for further use or analysis, making your process more efficient.
4. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: Use Cases
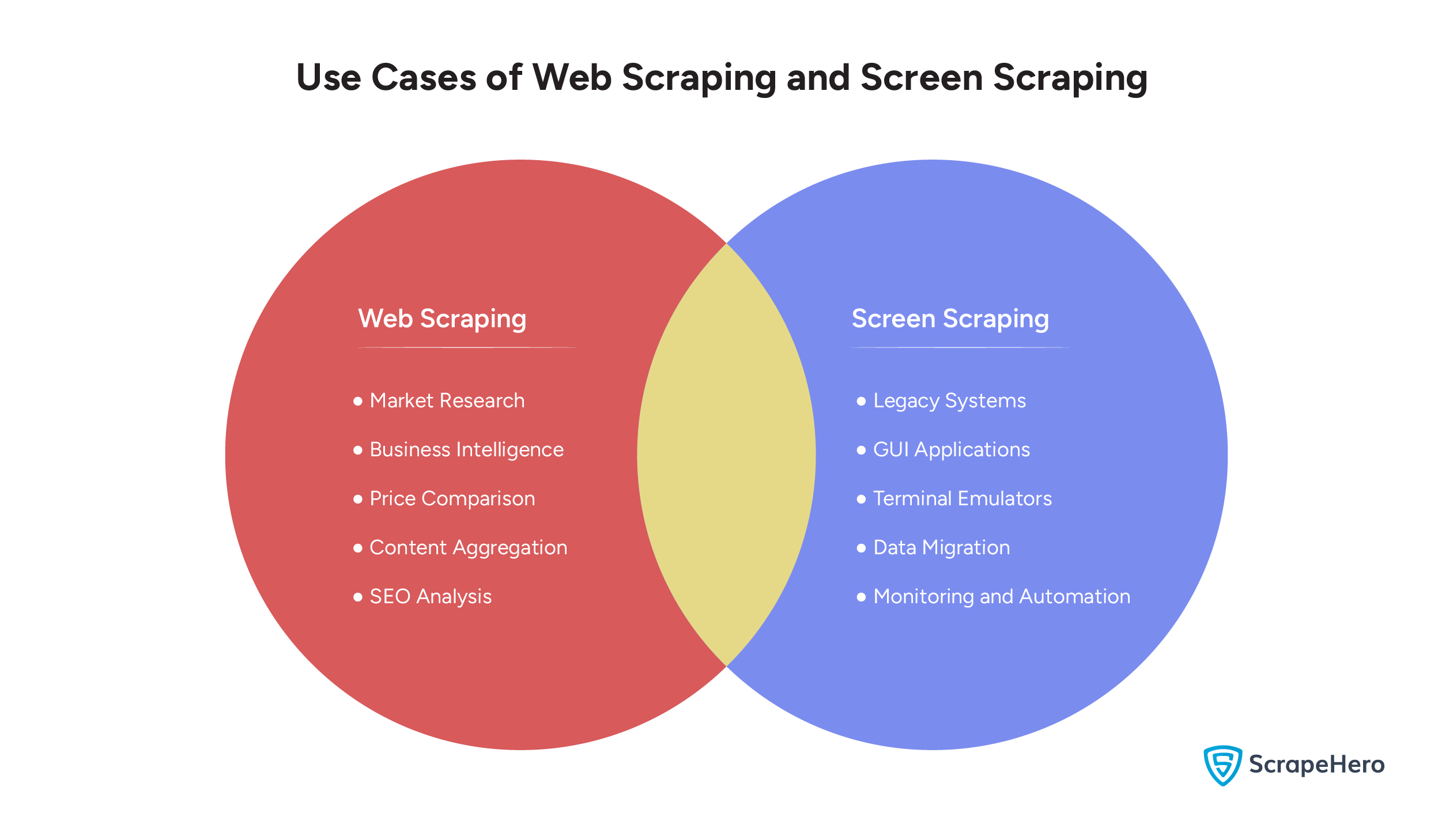
Use Cases for Web Scraping
Web scraping is used to periodically extract data from different sources to make informed data-driven decisions. Some of its use cases include:
- Market Research
- Business Intelligence
- Price Comparison
- Content Aggregation
- SEO Analysis
-
Market Research
Web scraping is used to gather data on market trends, competitor products, and customer preferences.
-
Price Comparison
You can compare the prices of products across different e-commerce platforms once data is obtained after web scraping.
If you want to gather pricing intelligence data and track your competitor products on various e-commerce platforms, you can use ScrapeHero’s Price Monitoring Service.
-
Content Aggregation
Web scraping is also a way to collect content from multiple websites for news aggregation, social media monitoring, and academic research.
-
SEO Analysis
The scraped data can be used to analyze search engine optimization metrics, like keyword rankings and backlinks.
-
Business Intelligence
Web scraping is a great choice for enterprises that need business intelligence to extract data for business analytics, reporting, and decision-making.
Use Cases for Screen Scraping
Screen scraping has been used in a vast number of fields. Some of its potential use cases include:
- Legacy Systems
- GUI Applications
- Terminal Emulators
- Data Migration
- Monitoring and Automation
-
Legacy Systems
Screen scraping is used to extract data from old or obsolete software that lacks modern APIs or data export capabilities.
-
GUI Applications
It is an excellent method to capture data from applications with graphical interfaces like desktop software and enterprise systems.
-
Terminal Emulators
Screen scraping is used to extract information from terminal-based applications and command-line interfaces.
-
Data Migration
Screen scraping is also used when you want to transfer data from one system to another in case direct database access is not available.
-
Monitoring and Automation
Automating repetitive tasks and monitoring application behavior by capturing screen outputs is another use case of screen scraping.
5. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: Key Similarities and Differences
Key Differences Between Web Scraping and Screen Scraping
|
Web Scraping |
Screen Scraping |
|
Retrieves data from HTML content |
Captures data from visual outputs |
|
Relies on parsing structured HTML |
More complex due to the need to interpret visual data |
|
More accurate and reliable |
Prone to errors due to various factors |
|
Handle larger volumes of data more efficiently |
Slower due to the need to process visual data |
Similarities Between Web Scraping and Screen Scraping
Web scraping and screen scraping share many common similarities. The major ones are in:
- Data Extraction
- Automation
- Applications
-
Data Extraction
Both web scraping and screen scraping aim to extract data from sources where direct access is not feasible.
-
Automation
Both methods use automation tools or scripts to capture and process data.
-
Applications
They both are used for purposes such as market research, competitive analysis, and data aggregation.
Differences Between Web Scraping and Screen Scraping
The primary difference between web scraping and screen scraping are in:
-
Data Source
Web scraping retrieves data from HTML content, while screen scraping captures data from visual outputs.
-
Complexity
Web scraping is less complex as it relies on parsing structured HTML, whereas screen scraping is more complex as it needs to interpret visual data.
-
Accuracy
Web scraping is more accurate and reliable, whereas screen scraping is prone to errors due to variations in screen resolution, layout, and other visual factors.
-
Performance
Web scraping is faster and handles large volumes of data, but screen scraping is slower due to the need to process visual data.
6. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: Tools Used
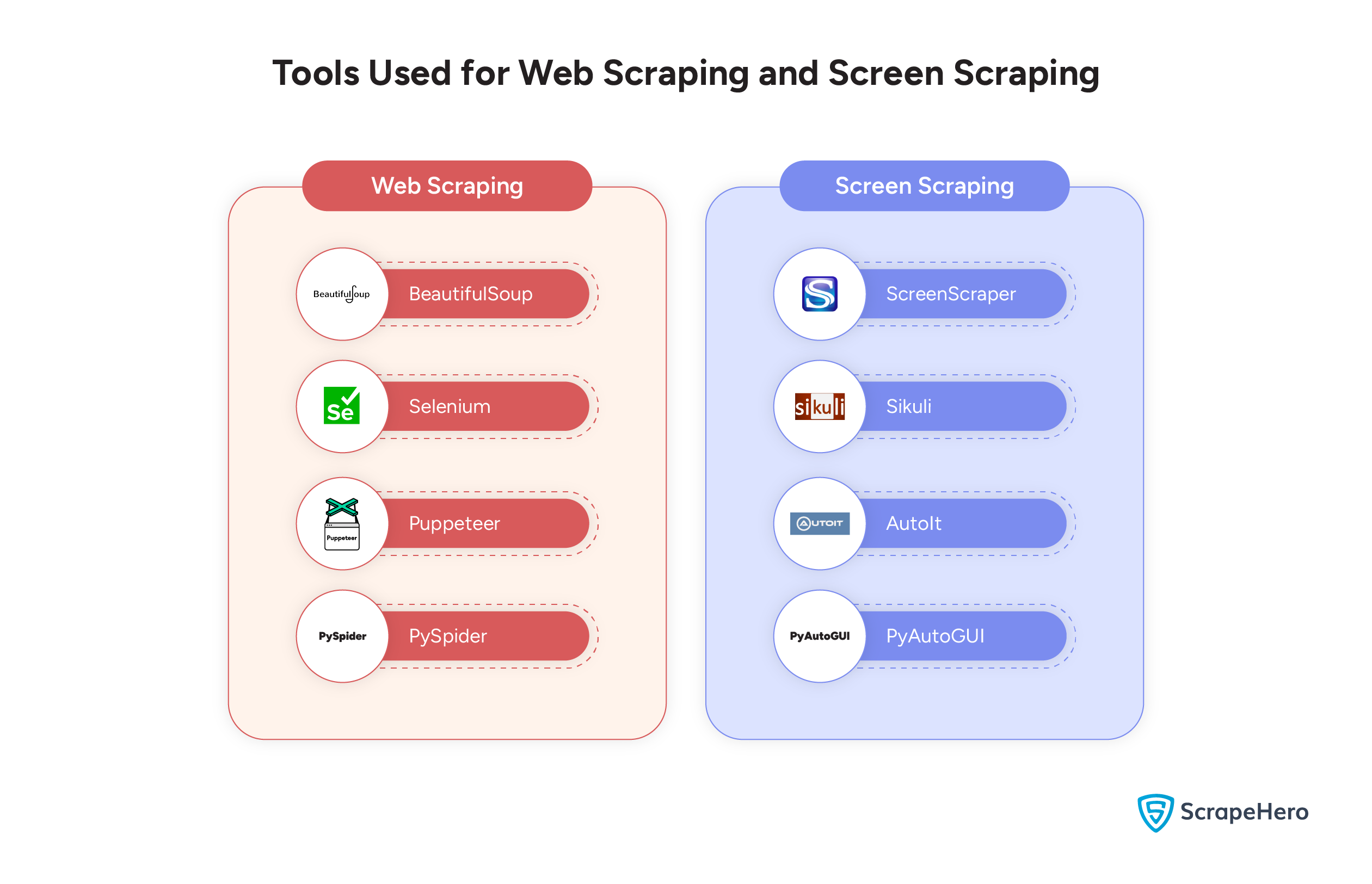
Web Scraping Tools
Open-source tools are an essential part of web scraping. Some of the prominent web scraping tools include:
- BeautifulSoup
- PySpider
- Selenium
- Puppeteer
-
BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup is a Python library used to parse HTML and XML documents and extract data.
-
PySpider
PySpider is a tool that supports JavaScript pages and has an easy-to-use UI for editing scripts, monitoring tasks, and viewing results.
-
Selenium
Selenium is used to automate web browsers and scrape dynamic content on the web.
-
Puppeteer
Puppeteer is a Node.js library that provides a high-level API for controlling headless Chrome or Chromium.
Screen Scraping Tools
Screen scraping tools can capture, automate, and extract data from the graphical user interface (GUI) of applications. Here are prominent tools:
- ScreenScraper
- Sikuli
- AutoIt
- PyAutoGUI
-
ScreenScraper
ScreenScraper is specifically designed for screen scraping. It can capture and extract data from various sources by simulating user actions.
-
Sikuli
Sikuli is a visual automation tool that uses image recognition to automate interactions with GUI applications.
-
AutoIt
AutoIt is a scripting language that is designed to automate the Windows GUI and general scripting.
-
PyAutoGUI
PyAutoGUI is a Python library for screen scraping. It simulates user actions and captures data from the screen.
7. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: Legality
The legality of web scraping and screen scraping is not easily defined. It depends on several factors, such as the website’s terms of service and the type of data being scraped.
When you attempt to scrape data from websites that violate their terms of service, it can lead to legal repercussions.
Extracting copyrighted content without permission is also considered a violation of the law, resulting in intellectual property infringement.
In both web scraping and screen scraping, extracting personal or sensitive data concerns privacy and may breach data protection regulations like the CCPA.
8. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: Main Challenges
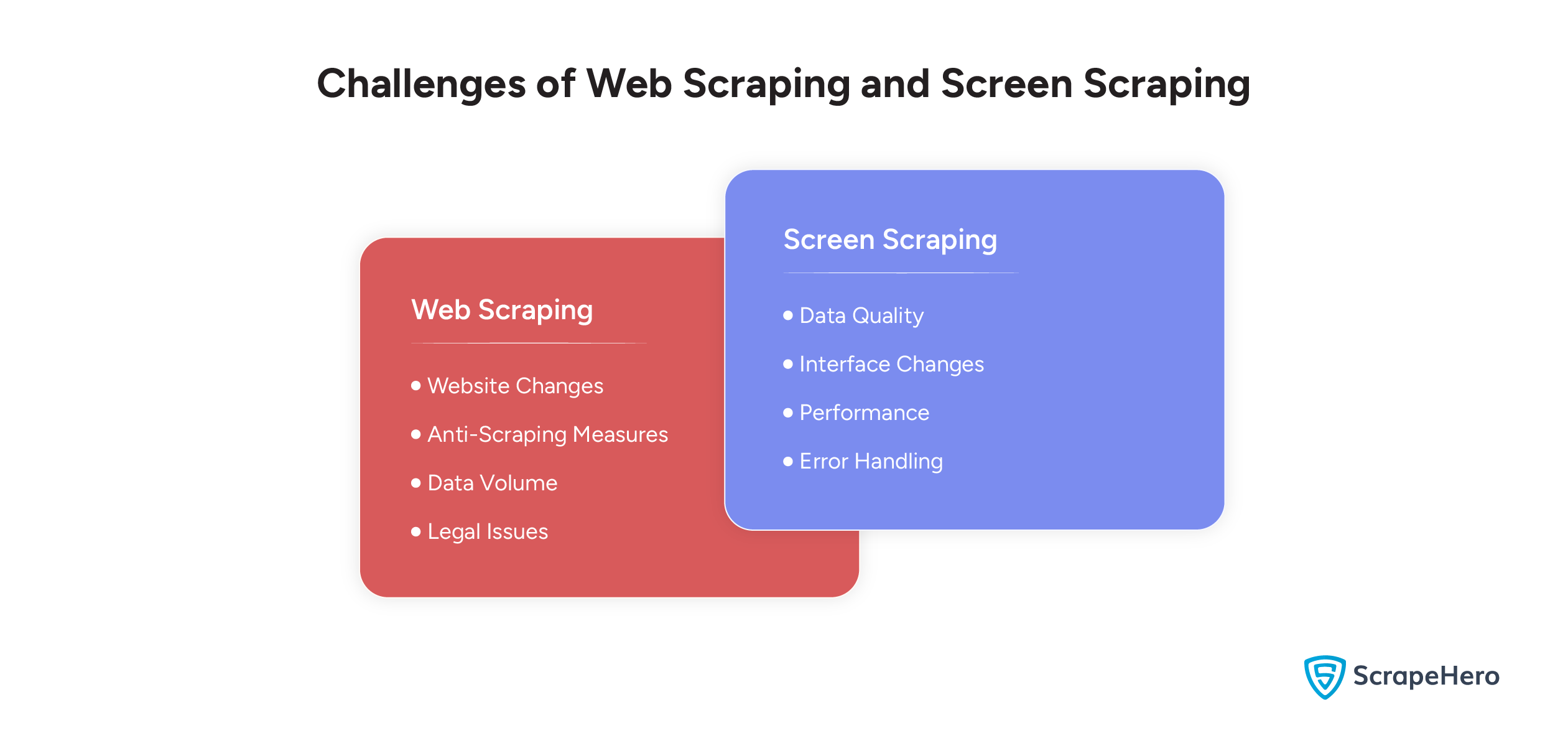
Web Scraping Challenges
Due to the complexity of technologies and the dynamic nature of the web, there are common web scraping challenges. These include:
- Website Changes
- Anti-Scraping Measures
- Data Volume
- Legal Issues
-
Website Changes
When websites frequently change their structure and layout, it becomes difficult for scrapers to access them, as they need to be constantly updated.
-
Anti-Scraping Measures
Websites prevent web scraping using various methods like IP blocking, user-agent filtering, and dynamic content loading.
-
Data Volume
When it comes to web scraping, it is challenging to handle large volumes of data efficiently and effectively.
-
Legal Issues
To navigate through the legal landscape and ensure ethical web scraping that compliance with terms of service and data protection regulations is also challenging.
Screen Scraping Challenges
Screen scraping can also pose a wide range of challenges due to the handling of visual data. These include:
- Data Quality
- Interface Changes
- Performance
- Error Handling
-
Data Quality
In screen scraping, the accuracy and consistency of extracted data from visuals are challenging.
-
Interface Changes
Sometimes, the GUI changes can break screen scraping scripts, which demand frequent updates.
-
Performance
For large-scale data extraction, screen scraping can be resource-intensive and slower when compared to web scraping.
-
Error Handling
Managing errors and exceptions in screen scraping is complex due to the variability of visual data.
9. Web Scraping vs Screen Scraping: Efficient Strategies
Strategies for Efficient Web Scraping and Screen Scraping
| Web Scraping | Screen Scraping |
| Respect Robots.txt | Modular Scripts |
| Rate Limiting | Error Handling |
| Dynamic Content Handling | OCR Optimization |
| IP Rotation | Automation Tools |
Efficient Web Scraping Strategies
For responsible data extraction, it is essential to follow proper web scraping guidelines. These can be:
- Respect Robots.txt
- Rate Limiting
- Dynamic Content Handling
- IP Rotation
-
Respect Robots.txt
To minimize the risk of being blocked, you should follow the guidelines listed in the website’s robots.txt file.
-
Rate Limiting
It is recommended to avoid loading the target website with requests, which may result in IP blocking.
-
Dynamic Content Handling
To handle dynamic content based on JavaScript execution, always use headless browsers such as Puppeteer or Selenium.
-
IP Rotation
To avoid detection and bypass anti-scraping methods, use proxies and IP rotation.
Efficient Screen Scraping Strategies
Screen scraping is majorly detected through a few given signatures or behaviors. Some techniques to avoid such detection include:
- Modular Scripts
- Error Handling
- OCR Optimization
- Automation Tools
-
Modular Scripts
Constantly develop modular scripts that are easy to update when the interface changes.
-
Error Handling
For ensuring data quality and managing exceptions, it is essential to implement robust error handling and logging.
-
OCR Optimization
Improve the text recognition accuracy by optimizing OCR settings and preprocessing images.
-
Automation Tools
It is better to use advanced automation tools for streamlining the screen scraping process and reducing manual intervention.
What Is RPA? How RPA Integrates With Web Scraping and Screen Scraping
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is a process automation technology for handling rule-based, repetitive tasks typically performed by humans.
Screen scraping is a subset of RPA. In fact, RPA, screen scraping, and web scraping are closely related technologies that complement each other in automation workflows.
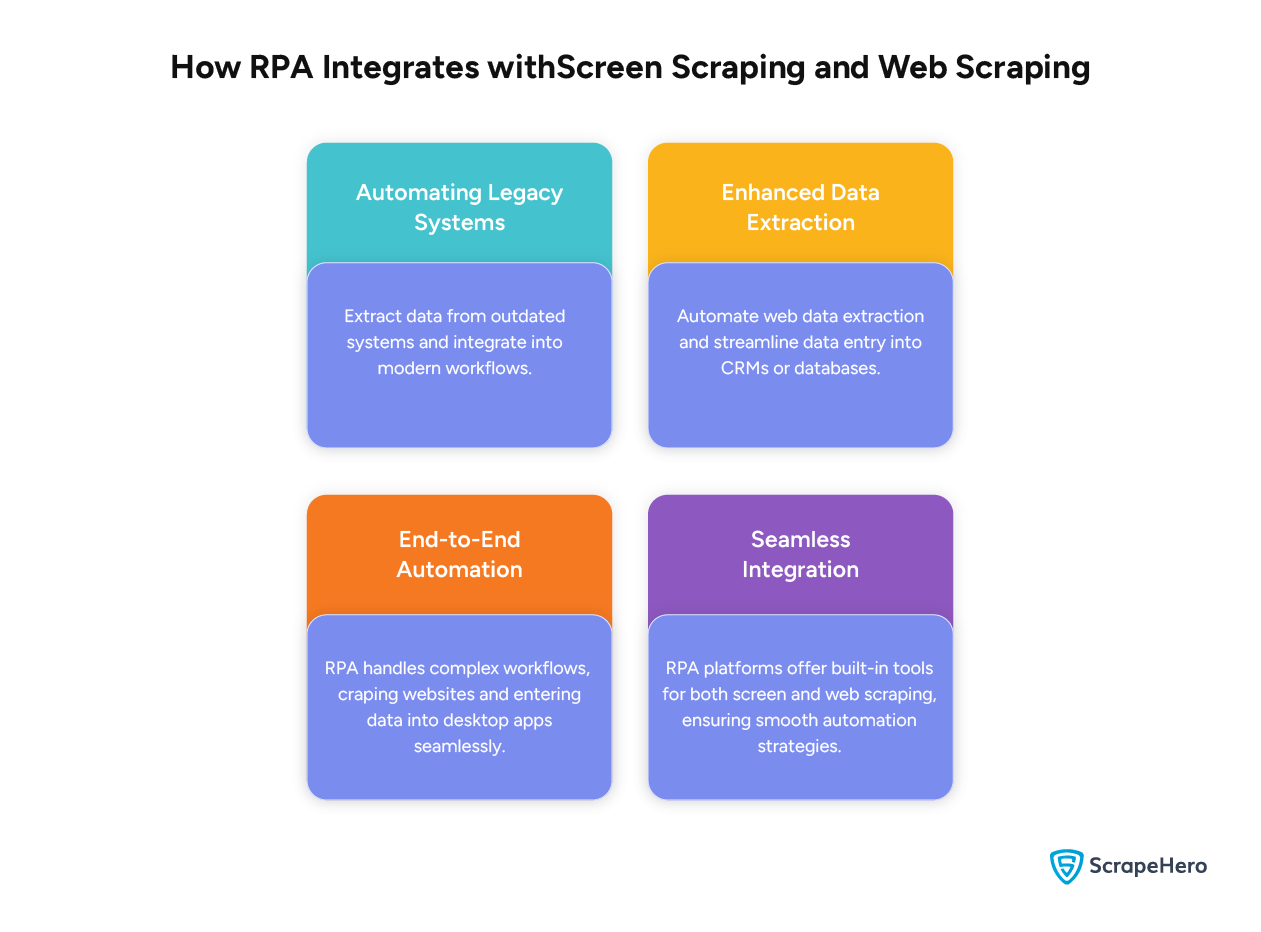
RPA integrates with web scraping and screen scraping through:
- Automating Legacy Systems
- Enhanced Data Extraction
- End-to-End Automation
- Seamless Integration
-
Automating Legacy Systems
RPA uses screen scraping to extract data from legacy systems without modern APIs. It can also integrate the data into more modern workflows.
-
Enhanced Data Extraction
When RPA is combined with web scraping, businesses can automate data extraction and subsequent processing, such as data entry into CRM systems or databases.
-
End-to-End Automation
RPA can handle complex workflows involving both web scraping and screen scraping. For example, it can scrape data from a website and then enter it into a desktop application.
-
Seamless Integration
In most cases, RPA platforms come with built-in capabilities for both web scraping and screen scraping, enabling broader automation strategies.
Why Choose ScrapeHero Web Scraping Services?
As technology evolves, data scraping requires techniques like advanced AI and machine learning, real-time data extraction, and cross-platform scraping.
Staying informed and adapting to these trends may be a hurdle for enterprises that focus on something other than data business but need vast amounts of data.
Whether it is handling the vast number of websites, the workforce required, or the speed and efficiency of crawling, ScrapeHero has it all.
We possess all the factors that enterprises seek in terms of technologies, skills, and experience.
At ScrapeHero, we understand the importance of cost-effectiveness. That’s why we handle massive scales while remaining affordable and effectively addressing all the unique challenges that come with web scraping.
Our global infrastructure, automated data quality checks, and transparent customer-centric approach help us retain our customers.
With a decade of experience in web scraping service and having worked with some of the biggest companies in most industries, we can help you satisfy your data needs by choosing the right scraping solution that fits your requirements.
Wrapping Up
Web scraping and screen scraping both can extract valuable data from different sources and have unique methods, applications, and challenges.
Contact ScrapeHero to overcome the challenges of web scraping and ensure the complete processing of the data pipeline and custom services for your businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
No. Although both sound similar and are used to extract data, they differ in various aspects.
Web scraping extracts data by parsing web pages’ HTML. On the other hand, screen scraping captures data directly from the screen display of an application.
No. Data scraping is the extraction of data from structured data sources like databases or spreadsheets.
Web scraping is the process of extracting unstructured data from websites using web scraping tools or software.
The legality of screen scraping depends on the context and its purpose. If it violates the terms of service or regulations, it can lead to legal action.
Screen scraping is used to extract data from the screen display, whereas OCR (Optical Character Recognition) converts text images into machine-readable format.
Scraping Amazon product prices and scraping Google Maps are all examples of web scraping.
Examples of screen scraping include automating data entry tasks in software applications and getting a live view of the global users of the website of a particular brand.
We can help with your data or automation needs
Turn the Internet into meaningful, structured and usable data