How do you write XPath for web scraping? Well, before that, you should understand what XPath is and how it works in the case of web scraping. XPath (XML Path) is a query language used to navigate XML or HTML documents. A concise XPath cheat sheet for web scraping can come in handy, especially when you want to extract specific data from web pages.
How Can You Get XPath?
To obtain XPath expressions for elements within a webpage, you can use the Developer Tools in modern web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge. Follow the steps mentioned to get the XPath for web scraping.
- Right-click on the webpage and select Inspect.
- Use the select tool to pick an element directly from the page.
- Right-click the highlighted HTML line in Developer Tools, go to Copy, and select Copy XPath or Copy full XPath.
XPath Basics
To learn more about web scraping using XPath, you need to first understand the basics of XPath using a simple example.
<div class="main">
<h1>
Bulbasaur
</h1>
<div id="description">
<p>
Bulbasaur can be seen napping in bright sunlight.
</p>
</div>
</div>
Accessing the data from HTML using XPath is easy. Let’s find <h1> from the above HTML using XPath.
The <h1> is located inside a <div> element with the class name “main”. The XPath for accessing the element will be:
//div[@class="main"]/h1The output produced is:
<h1> Bulbasaur </h1>
To access the text inside the <h1>
//div[@class="main"]/h1/text()
The output produced is:
BulbasaurLet’s consider a real-life interactive example so that you can understand the concept in depth. The screenshot shows the HTML structure of the web page, ScrapeMe.
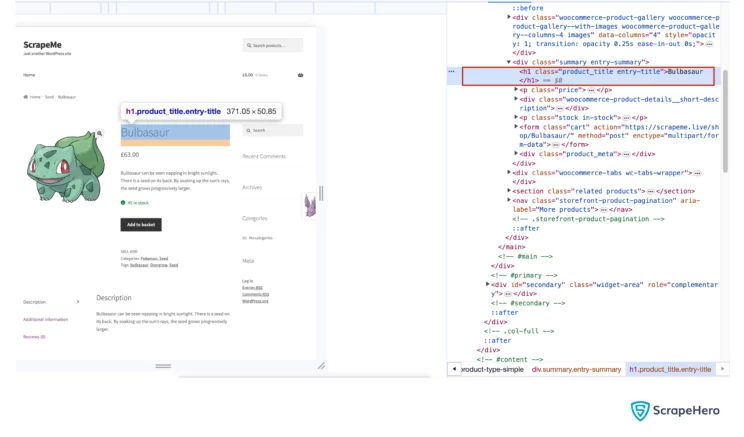
In this example, the <h1> is located inside a <div> element with the class name “summary entry-summary”. So the XPath for accessing the element will be:
//div[@class="summary entry-summary"]/h1The output produced is:
<h1> Bulbasaur </h1>
XPath Syntax
XPath expressions use a structure. Basically, there’s a root folder, and several directories are inside it. They may contain more folders. XPath traverses this tree to find the necessary elements that you target.
Or else you can say that XPath uses path expressions to find nodes in XML or HTML documents. The node is selected with a series of steps and axes. Here’s a breakdown of the XPaths used above.
//div[@class="main"]/h1
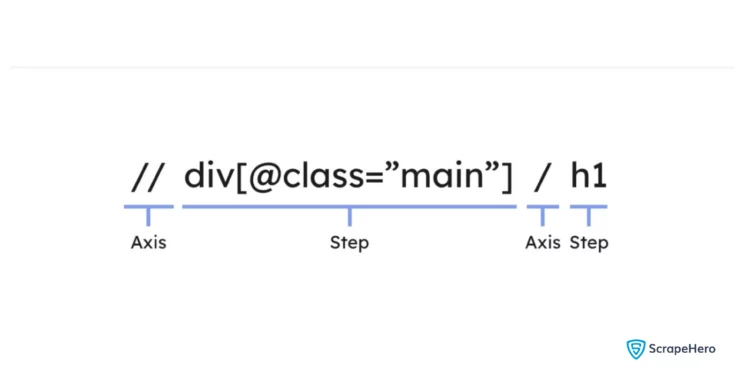
Axes – Axes can be used to locate nodes relative to the current node. Axes allow writing XPath to parse data from complex and nested documents. There are 13 distinct axes available for querying an element. They are used when you need to query for an element using its own attributes or when building hierarchical relationships.
Step – In XPath, step or path refers to the parts of an XPath expression that navigate through the nodes in an XML or HTML document. They define the route taken through the document’s structure to arrive at a specific node or set of nodes. In other words, a step or path contains the node that you would like to navigate to.
List of Most Commonly Used Expressions
Here’s an XPath cheat sheet that contains a list of some of the most commonly used XPath expressions. It can be very handy while navigating through and extracting data from XML or HTML documents.
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| // | Select any descendant of current node |
| / | Select any child of current node |
| . | Select current node |
| .. | Select the parent node |
| @ | Select attributes |
| nodename | Select matching nodes |
XPath Locators Cheat Sheet
Now let’s use the HTML given to create an XPath cheat sheet. In this way, you can learn web scraping using XPath much easier.
<html> <head></head> <body> <div class="main"> <h1>Bulbasaur</h1> <img src="..." alt="Bulbasaur" width="100" height="100" ><br> <label for="price">Price: </label> <span id="price">63.00</span> <br> <label for="sku">SKU: </label> <span id="sku">8783</span><br> <br> <strong>Description</strong> <div class="description"> <p> Bulbasaur can be seen napping in bright sunlight. There is a seed on its back. By soaking up the sun's rays, the seed grows progressively larger. </p> </div> <h4>Similar products</h4> <ul id="similar-products"> <li> <a href="...">Charmander</a> </li> <li> <a href="...">Venusaur</a> </li> <li> <a href="...">Ivysaur</a> </li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>
How to Select Nodes?
Selecting nodes in XPath involves writing expressions that match specific parts of an XML or HTML document. You can select nodes by their tag name, attribute values, specific content, or relationships to other nodes.
| XPath | Description | Output |
| //h1 | Selects all <h1> nodes | <h1>Bulbasaur</h1> |
| /html/body | Absolute path to <body> node | <body>…<body> |
| //div/span | Selects all <span> node that are children of a <div> node | <span id=”price”>63.00</span>
<span id=”sku”>8783</span> |
| /html/body/div/h1 | Absolute path to the <h1> node that is a child of <div> node | <h1>Bulbasaur</h1> |
| //div//a | Select all <a> nodes that are descendants of <div> nodes | <a href=”…”>Charmander</a>
<a href=”…”>Venusaur</a> <a href=”…”>Ivysaur</a> |
How to Select Attributes?
In XPath, selecting attributes involves writing expressions that specifically target the attributes of nodes. Attributes in XML and HTML are key-value pairs associated with elements, and you can select them directly or in the context of their elements.
| XPath | Description | Output |
| //@href | Selects all nodes’ href attribute | <a href=”…”>Charmander</a>
<a href=”…”>Venusaur</a> <a href=”…”>Ivysaur</a> |
| //div/@class | Select all <div> nodes’ class attribute | main
description |
| //a/text() | Select text content from all <a> nodes | Charmander
Venusaur Ivysaur |
Select Based on Order
In XPath, selecting nodes based on their order in the document is a common task, and you can do this using position predicates or functions. XPath provides several ways to select nodes based on their order or position among siblings or in a node-set.
| XPath | Description | Output |
| //li[1] | Selecting the first one from matching <li> nodes | <li> <a href=”…”>Charmander</a> </li> |
| //li[2] | Selecting the second one from matching <li> nodes | <li> <a href=”…”>Venusaur</a> </li> |
| //span[@id][2] | Select the first one from the <span> nodes with id attribute | <span id=”sku”>8783</span> |
| //li[last()] | Select the last node that from the matching <li> nodes | <li> <a href=”…”>Ivysaur</a> </li> |
Select Based on Node Relation
Selecting nodes based on their relationships to other nodes is a core feature that is useful when web scraping using XPath. It allows you to traverse the XML or HTML document tree in various directions.
| XPath | Description | Output |
| //label//following-sibling::span | Selecting the <span> node that is a following sibling of <label> | <span id=”price”>63.00</span>
<span id=”sku”>8783</span> |
| //label//following::p | Selecting the <p> nodes that follows <label> | <p> Bulbasaur can be… </p> |
| //label//preceding-sibling::img | Selecting the <img> node that is a preceding sibling of <label> | <img src=”…” alt=”Bulbasaur” width=”100″ height=”100″> |
| //a//parent::li | Select the parent <li> node of all <a> nodes | <li><a href=”…”>Charmander</a></li>…
<li><a href=”…”>Ivysaur</a></li> |
| //a//ancestor::ul | Select the ancestor <ul> node of all <a> nodes | <ul id=”similar-products”>…</ul> |
Miscellaneous
| XPath | Description | Output |
| //label[text()=”Price: “] | Text equals | <label for=”price”>Price: </label> |
| //a[contains(text(), “Charmander”)] | Substring selection | <a href=”…”>Charmander</a> |
| //span[contains(@class, “example”)] | String matching in class attribute | <div class=”description”> <p> … </p> </div> |
| //li[*] | Has children | <li> <a href=”…”>Charmander</a> </li>
<li> <a href=”…”>Venusaur</a> </li> <li> <a href=”…”>Ivysaur</a> </li> |
| //ul[li] | Has a specific tag as childrens | <ul id=”similar-products”> … </ul> |
| //a[text()=”Charmander” or text()=”Ivysaur”] | Or logic | <a href=”…”>Charmander</a>
<a href=”…”>Ivysaur</a> |
| //span[@id=”price”] | //span[@id=”sku”] | Union syntax. Join two results together. | <span id=”price”>63.00</span>
<span id=”sku”>8783</span> |
Axes
Axes can be used to locate nodes relative to the current node. Axes allow writing XPath to parse data from complex and nested documents.
Example usage: //span//following::p
In the XPath cheat sheet given, the keyword //following is an axis. It specifies to jump to the <p> node (::p) that follows the <span> node.
| Axis | Abbrev | Notes |
| ancestor | ||
| ancestor-or-self | ||
| attribute | @ | @href is short for attribute::href |
| child | /div is short for //child::div | |
| descendant | ||
| descendant-or-self | // | //h1 is short for /descendant-or-self::h1 |
| namespace | Selects all namespace nodes of the current node | |
| self | . | . is short for self::node |
| parent | .. | .. is short for parent::node |
| following | ||
| following-sibling | ||
| preceding | ||
| preceding-sibling |
What are the Limitations of Using XPath for Web Scraping
Web scraping using XPath offers several advantages but it has its own limitations and challenges. Some of them are:
-
Website Structure Changes
XPath expressions are highly dependent on the structure of the webpage. If the website’s layout or element attributes change, the XPath selectors may break, leading to the need for maintenance and updates in your scraping code.
-
Performance Issues on Large Documents
In complex or very large documents, using XPath can be less efficient than other methods. Complex XPath expressions may lead to performance issues, as they require traversing large parts of the document tree.
-
Limited Browser Support
Not all web browsers have the same level of support for XPath. While most modern browsers do support XPath, inconsistencies can occur, and some versions of Internet Explorer have limited or no support for XPath.
-
Complexity in Writing Expressions
Writing complex XPath expressions can be challenging, especially for beginners who look forward to web scraping using XPath. It requires a good understanding of the document structure and XPath syntax, which can have a steep learning curve.
-
Handling Dynamic Content
XPath does not inherently deal with dynamic content loaded through JavaScript. When scraping modern websites that heavily rely on JavaScript to render content, additional tools like Selenium or Puppeteer might be needed to ensure the content is loaded before using XPath to select elements.
Wrapping Up
The XPath cheat sheet given in the article can serve as a comprehensive guide for you to extract data from web pages efficiently, as it has covered important XPath features used in HTML parsing. While web scraping using XPath seems like a good option, you cannot be fully dependent on it, especially for large-scale web scraping.
Instead, if you have more specific needs, like scraping product data from Amazon, you can rely on ScrapeHero Amazon Product Details and Pricing Scraper from ScrapeHero Cloud. They are easy-to-use, affordable, fast, and reliable, offering a no-code approach to users without extensive technical knowledge.
If your needs are much larger, say enterprise-grade web scraping, you can consult ScrapeHero, as we can provide you with advanced, bespoke, and custom solutions. ScrapeHero web scraping services provide complete processing of the data pipeline, from data extraction to data quality checks, to boost your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How to add text in XPath?
In XPath, you don’t add text directly but rather use XPath to select nodes or elements based on their text content, or you retrieve the text content of nodes. However, you can construct XPath expressions that incorporate text conditions to precisely target nodes.
-
How to get data from XPath in Python?
When web scraping using XPath in Python, you can use libraries such as lxml or xml.etree.ElementTree to parse XML/HTML documents and retrieve data.
-
How to extract XPath from XML?
Extracting XPath from an XML document involves identifying the structure and hierarchy of the elements you want to target and then writing XPath expressions that match those elements. XPath does not generate automatically but is rather a way to query or navigate through the XML structure.
-
How do you scrape data using XPath in Python?
For web scraping using XPath in Python, you’ll typically use a combination of HTTP requests to fetch web pages and lxml for parsing the HTML content and executing XPath expressions.
We can help with your data or automation needs
Turn the Internet into meaningful, structured and usable data







