A proxy server, or simply a ‘proxy,’ acts as an intermediary between the user and the Internet and facilitates secure, anonymous, and unrestricted web access.
Depending on the needs, proxies are categorized into various types. This includes their configuration, the origin of their IP addresses, the flow of traffic they support, etc.
This article gives an overview of the different types of proxy servers that you can select to avoid potential financial losses and achieve the desired outcome.
Note: Throughout this article, the words proxies and proxy servers will be used interchangeably.
Types of Proxy Servers in a Computer Network
Before knowing the types of proxies used, you have to understand why you need a proxy for web scraping.
Proxies are required to avoid detection and blocking by websites during web scraping. If a user makes more requests per IP address in a short span than is possible, then there’s a possibility of getting banned.
To learn how websites detect the presence of bots, you can read our article on detecting bots using bot mitigation tools.
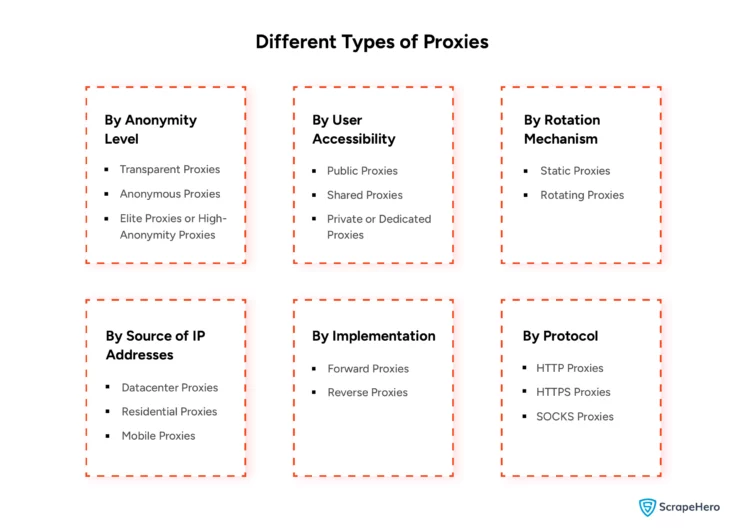
As mentioned earlier, proxies can be categorized according to various parameters.
- By Anonymity Level
- By User Accessibility
- By Rotation Mechanism
- By Source of IP Addresses
- By Implementation
- By Protocol
Let’s explore each category of proxies in detail, understanding their functionality and usability for multiple needs.
1. By Anonymity Level
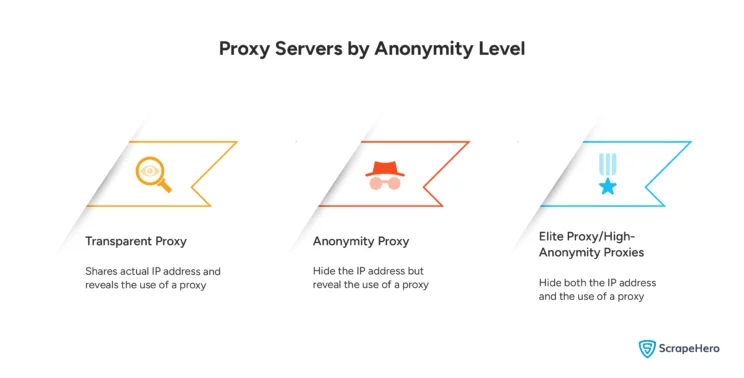
The anonymity level of proxies means how efficiently the proxies can hide the IP address and presence of proxy use from the destination server. They are classified into:
- Transparent Proxies
- Anonymous Proxies
- Elite Proxies or High-Anonymity Proxies
Let’s understand each such proxy in detail.
Transparent Proxies
These types of proxy servers do not provide anonymity; they share your real IP address with the destination server.
Since they make clear that you are using a proxy they are often used for content caching purposes rather than privacy.
Anonymous Proxies
These are the types of proxies that hide your IP address from the destination server.
Even though they offer a degree of anonymity, they might send HTTP headers that reveal the use of a proxy.
This proxy type may be suitable for users who want to avoid direct exposure to their IP but want to reveal that they are using proxies.
Elite Proxies or High Anonymity Proxies
These are among the best types of proxy that offer the highest level of anonymity as they hide both your IP address and the fact that a proxy is being used.
Since they leave no trace of proxy usage or your original IP, they are in great demand by users who need maximum privacy and security.
2. By User Accessibility
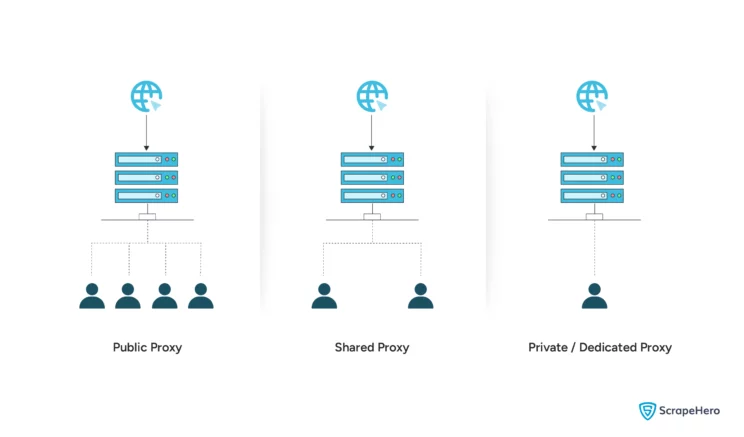
The user accessibility of proxies refers to the access of proxy servers to users. They are classified into:
- Public Proxies
- Shared Proxies
- Private or Dedicated Proxies
Public Proxies
These are available to anyone as free proxies for web scraping. They do not require authentication.
Since these proxies are freely available and convenient, they tend to be less reliable and more vulnerable to security risks.
Private or Dedicated Proxies
These types of proxy servers are allocated to a single user or organization.
These proxies provide high performance and improved security and are ideal for businesses or individuals with specific security requirements.
Shared Proxies
They are more affordable than private proxies and offer a balance between cost and performance. They are also more secure and reliable than public proxies.
3. By Rotation Mechanism
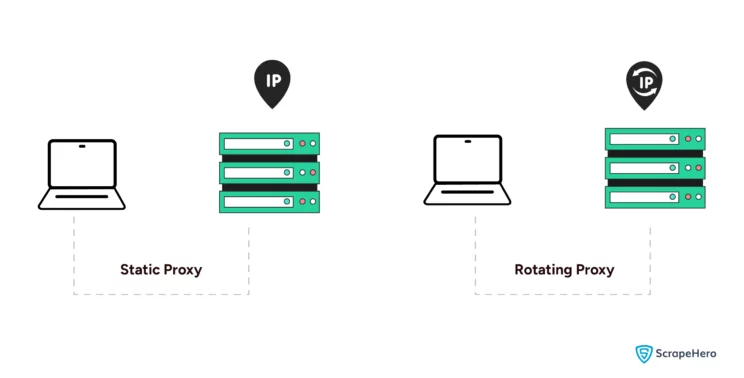
The rotation mechanism of proxies is defined as how proxy IP addresses are rotated to avoid detection. They are classified into:
- Static Proxies
- Rotating Proxies
Static Proxies
These types of proxy servers maintain the same IP address for each session. They are used for tasks that need a consistent identity, such as managing social media accounts.
Rotating Proxies
These proxies change IP addresses at each request or regular intervals. They are valid for web scraping and web crawling to avoid detection and IP bans.
4. By Source of IP Addresses
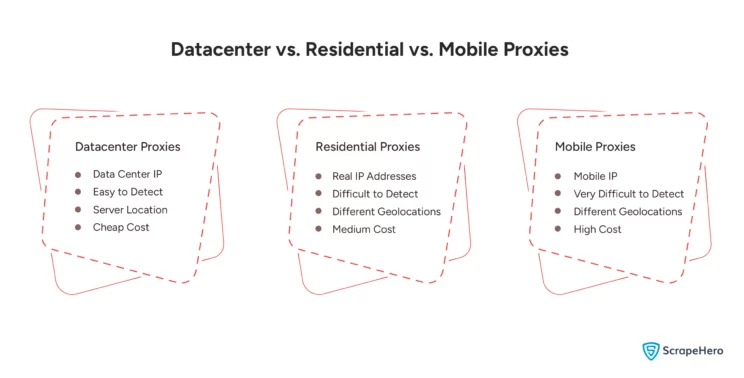
The source of IP addresses means the origin of the IP addresses. They are classified into:
- Datacenter Proxies
- Residential Proxies
- Mobile Proxies
Datacenter Proxies
These types of proxies are issued from servers in data centers and are known for their speed and efficiency.
Since they have non-residential IP addresses, they are easily detected by websites.
Residential Proxies
They are the best type of proxy since they use IP addresses assigned to private residences. Because of this, websites are less likely to block them.
If tasks require a higher degree of legitimacy, then these proxies are ideal.
Mobile Proxies
These kinds of proxies use IP addresses from mobile networks. Due to the diversity and dynamism of mobile IPs, they are highly effective at avoiding detection.
5. By Implementation
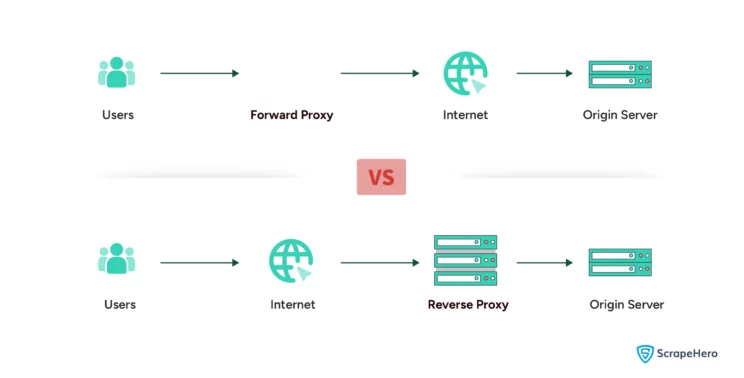
The implementation of proxies can be described as the methods by which proxies handle and route traffic. They are classified into:
- Forward Proxies
- Reverse Proxies
Forward Proxies
These types of proxies are situated between the client and the Internet. They fetch data from the Internet on behalf of a user or a network.
Reverse Proxies
These proxies operate on behalf of servers. They accept connections and pass them along.
They also enhance security, load balancing, and cache static content in server setups.
6. By Protocol
The protocol of proxies refers to the types of network protocols they support for handling traffic. They are classified into:
- HTTP Proxies
- HTTPS Proxies
- SOCKS Proxies
HTTP Proxies
These proxies are designed to handle HTTP protocol traffic, making them ideal for basic web browsing and content filtering.
They do not encrypt data, operate at the application layer, and are specifically tailored for managing web traffic.
HTTPS Proxies
These proxies are similar to HTTP proxies but support the HTTPS protocol, adding SSL encryption to ensure secure and encrypted data transmission.
Due to the encryption process, they are slightly slower. They also operate at the application layer, enhancing security.
SOCKS Proxies
These types of proxies can handle various types of TCP/IP traffic beyond HTTP/HTTPS, such as FTP and P2P.
They offer broad compatibility and flexibility but lack specific performance optimizations like caching, which can affect speed.
|
Feature |
HTTP Proxies |
HTTPS Proxies |
SOCKS Proxies |
|
Protocol Support |
HTTP only |
HTTPS (secure HTTP) |
All TCP/IP (e.g., HTTP, HTTPS, FTP) |
|
Security |
None |
Encrypted data |
No inherent encryption |
|
Performance |
Can modify data |
Slower due to SSL |
No data modification, versatile |
|
Use Cases |
Basic web browsing |
Secure data transfer |
Multiple protocols, secure sessions |
|
Connection Layer |
Application |
Application |
Session (more general tunneling) |
Wrapping Up
Proxies offer enhanced security and can overcome geographical barriers. However, choosing the right type of proxy according to the specific requirements can be challenging for enterprises.
These challenges are quickly resolved by ScrapeHero offering more sophisticated services and products like ScrapeHero Cloud.
In the rapidly evolving technological landscape, efficient data handling is crucial. ScrapeHero web scraping services are designed to provide proper solutions and effectively tackle emerging digital challenges, ensuring the highest data quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
Two main types of proxy servers are used for web scraping: Residential Proxies and Datacenter Proxies.
Residential Proxies provide genuine IP addresses that mimic user behavior, whereas Datacenter Proxies have high speed and cost efficiency but a higher risk of being blocked.
The best type of proxy depends on your specific needs. Generally, Residential Proxies are considered best as they are ideal for high anonymity and avoiding detection when web scraping.
The most common proxy type is the HTTP Proxy, widely used for general web browsing and simple content-filtering tasks.
To use a proxy IP for web scraping, you must configure your scraping tool to route requests through the proxy server.
This is done to mask your IP and avoid website detection and blocking.
Proxies are better than VPNs for web scraping as they provide IP rotation and more control over geographic targeting.
VPNs offer broader privacy but cannot be used for large-scale web scraping.
Different types of proxies used in cybersecurity, include Forward Proxies and Reverse Proxies.
Forward Proxies are used for client-side protection and anonymity, whereas Reverse Proxies are used for protecting and load-balancing server-side traffic.
Different types of proxies used in networking include Forward Proxies, Reverse Proxies, and Transparent Proxies.
We can help with your data or automation needs
Turn the Internet into meaningful, structured and usable data