A browser-based web scraper can be defined as a program that is used to extract data from websites with the help of a web browser that can navigate and interact with the web pages. Playwright web scrapers must be optimized with code profiling tools, as they consume a lot of resources and take longer to render than other types.
You have already learned about building web scrapers quickly using Playwright Codegen. In this article, you will learn how to optimize browser-based web scrapers with code profiling.
Code profiling tools are used to identify the parts of the code that need improvement. Later, optimization techniques are implemented to reduce resource consumption and speed up rendering time.
What is Code Profiling?
Code profiling is a technique for measuring the performance and resource usage of software applications. It involves analyzing the execution of the code and collecting data about running time, memory usage, and the frequency of function calls.
With the information collected by using code profiling tools, one can identify the bottlenecks and optimize the code for improved performance and efficiency.
Code profiling and software profiling are closely related terms. Software profiling is a broader concept that involves the entire software application to evaluate performance, find issues, or assess the user experience. Whereas code profiling is a subset of software profiling.
When choosing software profiling tools, consider factors such as ease of use, customization options, and compatibility with your development environment. Some common software profiling tools used are Valgrind, Heaptrack, JProfiler, Dynatrace, etc.
Similarly, for profiling the Python code, various Python profiling tools are used. Below are some of the popular tools used for Python code optimization:
- PyInstrument
- cProfile
- PyCharm Profiler
- Yappi
- SnakeViz
- PySpeedIT
- Pyflame
- FunctionTrace
- Palanteer
- Py-Spy
Each tool has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice will depend on your specific needs and requirements. Some Python profiling tools, like cProfile and PyInstrument, are great for simple profiling needs, while others, like PyCharm Profiler, are more advanced and provide a wide range of profiling features and options.
Throughout this article, one of the prominent Python profiling tools, PyInstrument, will be mentioned.
Create a scraper
To begin, let’s create a scraper with the below steps:
- Go to the start page – https://scrapeme.live/shop/
- Extract data from all product pages.
- Paginate up to 5 listing pages and extract the product details.
You can find the entire code below:
from playwright.sync_api import Playwright, sync_playwright
import time
def extract_data(page):
print(f"Extracting data for {page.url}")
# we are using sleep instead of extracting all the data
time.sleep(2)
def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
browser = playwright.chromium.launch(headless=False)
context = browser.new_context()
# Open new page
page = context.new_page()
# Go to https://scrapeme.live/shop/
page.goto("https://scrapeme.live/shop/")
# collect all product data
products = page.locator('li.product')
for i in range(products.count()):
product = products.nth(i)
with page.expect_navigation():
product.click()
extract_data(page)
page.go_back()
# Click text=→ nth=0
max_pagination = 5
for i in range(max_pagination):
page.locator("text=→").first.click()
# collect all product data
products = page.locator('li.product')
for i in range(products.count()):
product = products.nth(i)
with page.expect_navigation():
product.click()
extract_data(page)
page.go_back()
# ---------------------
context.close()
browser.close()
with sync_playwright() as playwright:
run(playwright)
To optimize the performance of the scraper code, we will now profile it.
First, install Pyinstrument using pip.
pip3 install pyinstrument
To use the profiler, let’s make some changes to the scraper.
Import the Profiler class from the module.
from pyinstrument.profiler import Profiler
Wrap the run function call with
with sync_playwright() as playwright:
with Profiler() as profiler:
run(playwright)
profiler.open_in_browser()
Run the scraper.
python3 slow_scraper.py
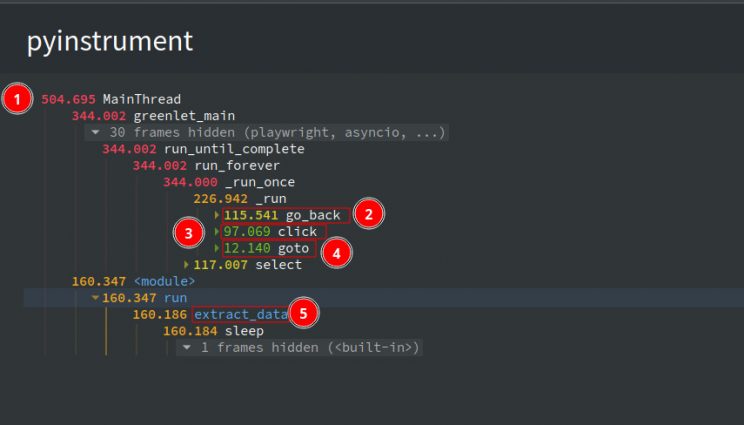
Once the script is finished, the results will open in your browser.
- The total time taken is 504.6 seconds
- The time taken for go_back action is 115.5 seconds
- The time taken for click action is 97 seconds
- The time taken for goto action 12.1 seconds
- The time taken for the extract_data function is 160 seconds
Let’s try to speed this up.
Optimize the Scraper
Synchronous to Asynchronous Playwright API
As you can see, the spider is using the Playwright Synchronous API. So first, change it to the Asynchronous API. See the code below:
from playwright.async_api import Playwright, async_playwright
import asyncio
async def extract_data(page):
print(f"Extracting data for {page.url}")
# we are using sleep instead of extracting all the data
await asyncio.sleep(2)
async def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
browser = await playwright.chromium.launch(headless=False)
context = await browser.new_context()
# Open new page
page = await context.new_page()
# Go to https://scrapeme.live/shop/
await page.goto("https://scrapeme.live/shop/")
# collect all product data
products = page.locator('li.product')
for i in range(await products.count()):
product = products.nth(i)
async with page.expect_navigation():
await product.click()
await extract_data(page)
await page.go_back()
# Click text=→ nth=0
max_pagination = 5
for i in range(max_pagination):
await page.locator("text=→").first.click()
# collect all product data
products = page.locator('li.product')
for i in range(await products.count()):
product = products.nth(i)
async with page.expect_navigation():
await product.click()
await extract_data(page)
await page.go_back()
# ---------------------
await context.close()
await browser.close()
async def main():
async with async_playwright() as playwright:
await run(playwright)
asyncio.run(main())
Let’s add the code to profile the script to the mainfunction.
async def main():
async with async_playwright() as playwright:
with Profiler() as profiler:
await run(playwright)
profiler.open_in_browser()
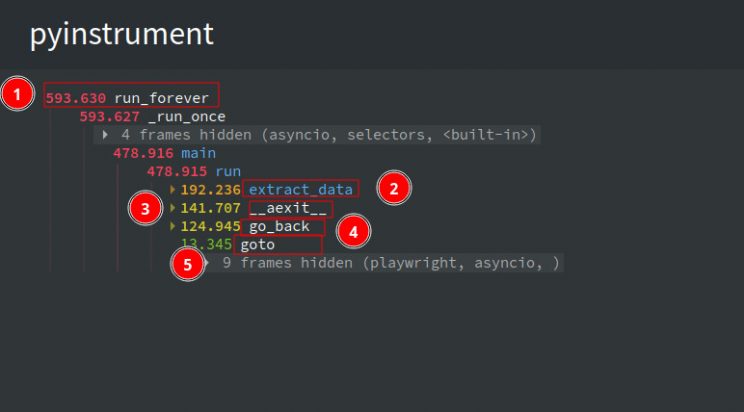
If we rerun the script we get the following output –
- The total time taken for the script to complete is 593.6 seconds
- The time taken for extract_data to complete is 192.2 seconds
- The time taken for
__aexit__to complete is 141.7 seconds. - The time taken for go_back to complete is 124.9 seconds
- The time taken for goto to complete is 13.3 seconds.
The __aexit__ shown in the logs is the time taken to complete the clicks. The clicks are surrounded by an async context manager, as shown below. This is why instead of click, it shows __aexit__
async with page.expect_navigation():
await product.click()
Unfortunately, the switch to an Asynchronous API does not result in the desired improvement in speed. The data collection process remains sequential, leading to slower overall performance. However, with further modifications, it is possible to achieve concurrent data collection, thereby enhancing the speed of the scraper.
Clean the Code
Before doing that, some other issues in the code must be fixed. The code block for processing the listing page is repetitive. This can be fixed by adding a new function:
async def process_listing_page(page):
"""Extract data from a single listing page"""
products = page.locator('li.product')
for i in range(await products.count()):
product = products.nth(i)
async with page.expect_navigation():
await product.click()
await extract_data(page)
await page.go_back()
Change the run function accordingly.
async def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
browser = await playwright.chromium.launch(headless=False)
context = await browser.new_context()
# Open new page
page = await context.new_page()
# Go to https://scrapeme.live/shop/
await page.goto("https://scrapeme.live/shop/")
# collect all product data
await process_listing_page(page)
# Click text=→ >> nth=0
max_pagination = 5
for i in range(max_pagination):
await page.locator("text=→").first.click()
# collect all product data
await process_listing_page(page)
# ---------------------
await context.close()
await browser.close()
The run function is much cleaner now.
For paginating, you can click on the next button. If you look at the paginated URLs, you can see that only the page number is changing.
You can create the pagination URL by changing the page number at the end. An example is shown below:
https://scrapeme.live/shop/page/{page_no}
async def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
browser = await playwright.chromium.launch(headless=False)
context = await browser.new_context()
# Open new page
page = await context.new_page()
max_pagination = 5
# list is initialised with starting url
listing_urls = ["https://scrapeme.live/shop/"]
for page_no in range(2, max_pagination + 2):
listing_urls.append(f"https://scrapeme.live/shop/page/{page_no}")
for url in listing_urls:
await page.goto(url)
await process_listing_page(page)
# ---------------------
await context.close()
await browser.close()
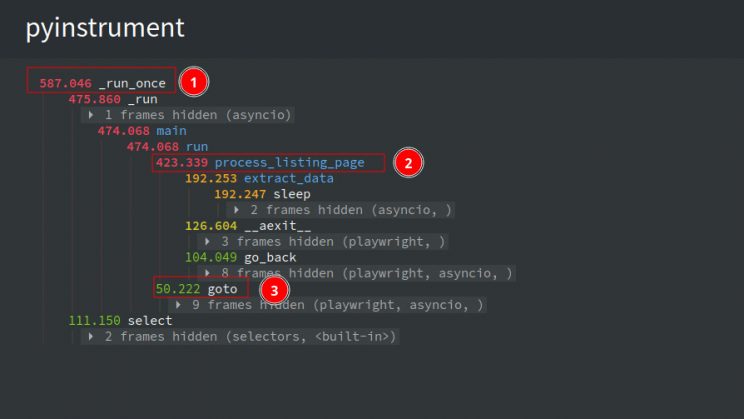
Let’s profile the code again and see if there are any improvements.
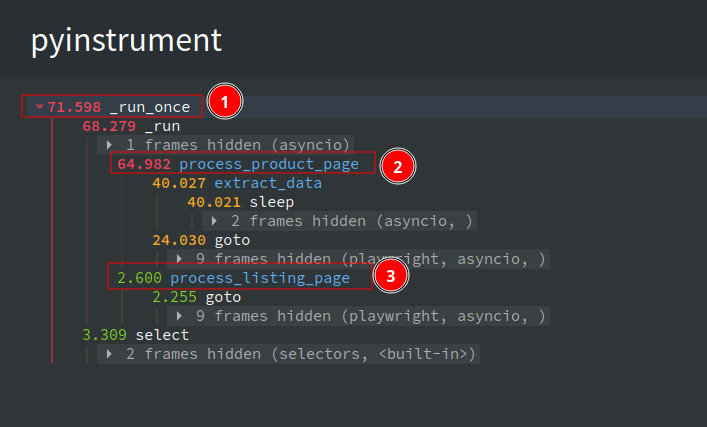
You can see that there’s no improvement in the overall runtime, with the process_listing_page taking the majority of the time. Most of this time is spent waiting for the coroutines to finish, as indicated by the wait time on select. To reduce this wait time, you can process the pages concurrently.
Instead of handling product pages by clicking on each item individually, changing the approach will be a wise choice. First, visit each listing page and collect all product URLs. Then, process all the URLs together, resulting in a more efficient process.
Make the changes to the function process_listing_pages.
async def process_listing_page(context, url):
"""Extract data from a single listing page"""
page = await context.new_page()
await page.goto(url)
products = page.locator('li.product a[class*=product__link]')
product_anchor_elements = await products.element_handles()
product_urls = await asyncio.gather(*[
i.get_attribute('href') for i in product_anchor_elements
])
await page.close()
return product_urls
Add a new function to handle product pages.
async def process_product_page(context, url):
page = await context.new_page()
await page.goto(url)
await extract_data(page)
await page.close()
Modify the run function accordingly.
async def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
browser = await playwright.chromium.launch(headless=False)
context = await browser.new_context()
max_pagination = 5
listing_urls = ["https://scrapeme.live/shop/"]
for page_no in range(2, max_pagination + 2):
listing_urls.append(f"https://scrapeme.live/shop/page/{page_no}")
product_urls = []
for url in listing_urls:
product_urls.extend(await process_listing_page(context, url))
for url in product_urls:
await process_product_page(context, url)
# ---------------------
await context.close()
await browser.close()
Process Pages Concurrently
As you may have noticed in the code above, the browser context is passed to each of the functions that process the pages. These functions use the context object to create a new page whenever necessary, allowing us to concurrently process multiple pages.
Now modify the run function to process these concurrently by using asyncio.gather.
async def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
browser = await playwright.chromium.launch(headless=False)
context = await browser.new_context()
max_pagination = 5
listing_urls = ["https://scrapeme.live/shop/"]
for page_no in range(2, max_pagination + 2):
listing_urls.append(f"https://scrapeme.live/shop/page/{page_no}")
product_urls = []
listing_coro = []
for url in listing_urls:
listing_coro.append(process_listing_page(context, url))
# product urls will be a list containing list of urls
product_urls = await asyncio.gather(*listing_coro)
product_coros = []
# using itertools.chain to loop over product urls
for url in itertools.chain(*product_urls):
product_coros.append(process_product_page(context, url))
# ---------------------
await context.close()
await browser.close()
The current implementation has a scalability issue where the number of pages opened increases with the number of URLs processed concurrently. This can lead to resource exhaustion and slow down the system. To address this, introduce a Semaphore to limit the number of concurrent processes being executed.
A Semaphore is a synchronization primitive that controls access to a shared resource through the use of a counter.
In this case, the shared resource is the number of concurrent processes. By limiting the number of concurrent processes, the Semaphore helps to prevent resource exhaustion and maintain system performance.
Create and add a semaphore object to all the functions that create a new page.
Create a semaphore with a max concurrency of 5.
sem = asyncio.Semaphore(5)
Modify the process_product_page function
async def process_listing_page(context, url, sem):
"""Extract data from a single listing page"""
async with sem:
page = await context.new_page()
await page.goto(url, timeout=60000)
products = page.locator('li.product a[class*=product__link]')
product_anchor_elements = await products.element_handles()
product_urls = await asyncio.gather(*[
i.get_attribute('href') for i in product_anchor_elements
])
await page.close()
return product_urls
The finalized run function looks like this
async def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
browser = await playwright.chromium.launch(headless=False)
context = await browser.new_context()
max_pagination = 5
sem = asyncio.Semaphore(5)
listing_urls = ["https://scrapeme.live/shop/"]
for page_no in range(2, max_pagination + 2):
listing_urls.append(f"https://scrapeme.live/shop/page/{page_no}")
product_urls = []
listing_coro = []
for url in listing_urls:
listing_coro.append(process_listing_page(context, url, sem))
# product urls will be a list containing list of urls
product_urls = await asyncio.gather(*listing_coro)
product_coros = []
# using itertools.chain to loop over product urls
for url in itertools.chain(*product_urls):
product_coros.append(process_product_page(context, url, sem))
await asyncio.gather(*product_coros)
# ---------------------
await context.close()
await browser.close()
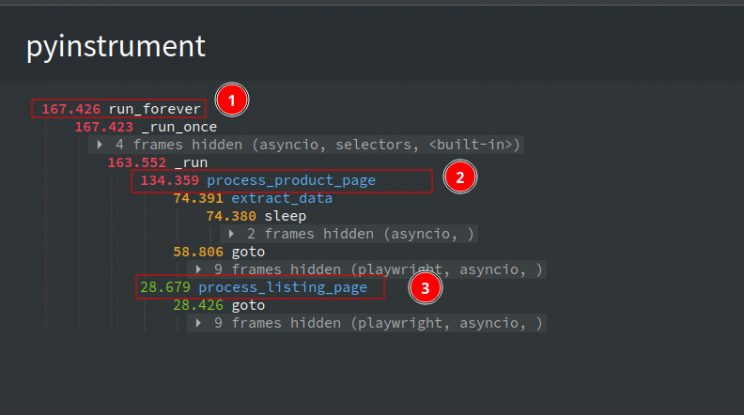
Let’s profile the final code.
The average time taken to complete the entire scrape was 167.4 seconds. Previously it was around 500 seconds- a 66.6 % reduction in run time.
If you check the profiler output, you can see that the process_product_page took most of the time (134.4 seconds) to complete processing. This can be further reduced by using Request Interception to block unwanted requests.
Add Request Interception
Add a function intercept that blocks all images, stylesheets, fonts, and scripts.
async def intercept(route):
if route.request.resource_type in {"stylesheet", 'image', 'fonts', 'script'}:
await route.abort()
else:
await route.continue_()
Modify the run function accordingly.
async def run(playwright: Playwright) -> None:
browser = await playwright.chromium.launch(headless=False)
context = await browser.new_context()
# request interception
await context.route('**/*', intercept)
...
Interception can be added to specific page objects as well, but in this case, adding once to context makes the interception available for all child pages.
Now run and profile the scraper and see if it has any effect.
The time for the entire scrape has been reduced to 71.5 seconds. Comparing it with the initial script, the script only takes 14.3% of the time now.
A similar approach can be taken on many scraping projects to improve the run time. In the above example, a single function is divided into smaller functions and executed concurrently. Then a request interception is added to drop unwanted requests. The final scraper runs around 7 times faster than the original one.
Optimized Code
You can get the fully optimized code in Python and JavaScript by referring to the below-mentioned links.
Python
JavaScript
Wrapping Up
Code profiling determines where a component or line of code is consuming resources, and for this, code profiling tools such as PyInstrument, cProfile, etc. are used. It is essential that you choose the right tool according to the situation.
Through this article, you have already got an idea about identifying the bottlenecks of your scraper and optimizing it for improved performance and efficiency.
ScrapeHero, a reliable data service provider, can streamline the web scraping process for enterprises. Let’s meet if your needs include customized data solutions for Brand Monitoring, Alternative Data, Location Intelligence, and much more.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the most efficient language for web scraping?
Python is the most efficient programming language for web scraping due to its vast collection of libraries and tools, such as BeautifulSoup and Requests. Python has a simple syntax, which makes it an even better choice for beginners. Other language choices include Node.js, Java, PHP, Ruby, R, Go, etc. - What is profiling in testing?
‘Software profiling’ or simply ‘profiling’ in software testing means to measure and analyze runtime statistics to find out performance bottlenecks. It measures memory, the time complexity of the program, the duration of function calls, or the usage of specific instructions. Some software profiling tools include Pyroscope, Pyinstrument, Scalene, VisualVM, etc. - What are the common Python profiling tools?
Python profiling tools must be used according to the needs of the user. For example, standard library modules like time and timeit can be used for basic timing, or cProfile can be used for the collection of detailed statistics. Some other Python profiling tools include PyInstrument, PyCharm Profiler, Yappi, SnakeViz, FunctionTrace, etc. - What are the benefits of code profiling?
With code profiling, software development cycles become shorter and much more agile. It also allows developers to profile the code at every stage of development. Code profiling enables the application to perform well under all circumstances, along with enabling the developers to fix anomalies in real-time. - Is Playwright good for web scraping?
Yes, Playwright is a good solution for web scraping as it is easy to use and allows for fast deployment and execution. It provides automation capabilities and allows users to perform tasks with minimal human input. - Is Playwright faster than Selenium?
Yes. Playwright generally offers better performance and speed compared to Selenium due to its easy-to-use API, auto-waiting capabilities, etc. For instance, Playwright’s auto-waiting function eliminates the need for manual waiting and reduces the chances of timing-related issues. - How do you scrape a web with Playwright in Python?
Web scraping with Playwright in Python involves several steps, including installation of the package, launch of a browser, navigation of the web page, interaction with the page elements, and extraction of the data.