Your biggest competitive advantage might also be your biggest security risk.
Web scraping gives businesses powerful insights into markets, competitors, and opportunities. But when companies outsource this critical function, they often hand over their most sensitive strategic information to vendors they’ve never fully vetted.
The result?
The same data that should give you an edge could be the thing that destroys it.
So, here’s the question that keeps security-focused executives up at night: How do you get the competitive advantage of web scraping without exposing your most valuable secrets?
The answer isn’t simple, and outsourced web scraping security is a complex challenge that requires careful consideration.
In this article, we’ll explain the risks of outsourcing web scraping and the compliance and security checks every business should demand. Also, we’ll discuss how to choose a partner that keeps your data and reputation safe.

Why Outsourced Web Scraping Security Matters
The High Stakes of Scraped Data
Web scraping today involves much more than collecting public information. Businesses use scraped data for competitive intelligence, market analysis, and customer insights. This data often reveals business strategies, target markets, and priorities that competitors would pay big money to access.
For example, your scraped data might show:
- Which markets are you researching for expansion
- Your pricing strategy analysis patterns
- Which competitors are you watching
- Customer acquisition targets
When this information goes through an unsafe vendor’s systems, you’re basically sharing your strategic plans.
Why worry about expensive infrastructure, resource allocation and complex websites when ScrapeHero can scrape for you at a fraction of the cost?Go the hassle-free route with ScrapeHero
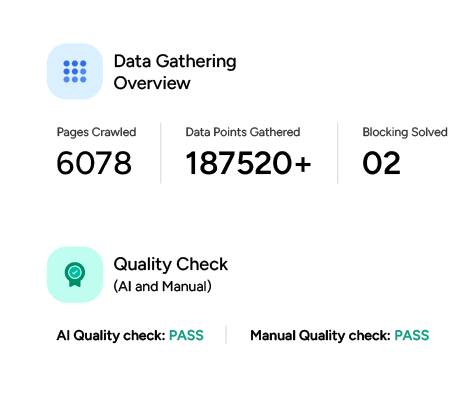
The High Cost of Security Failures
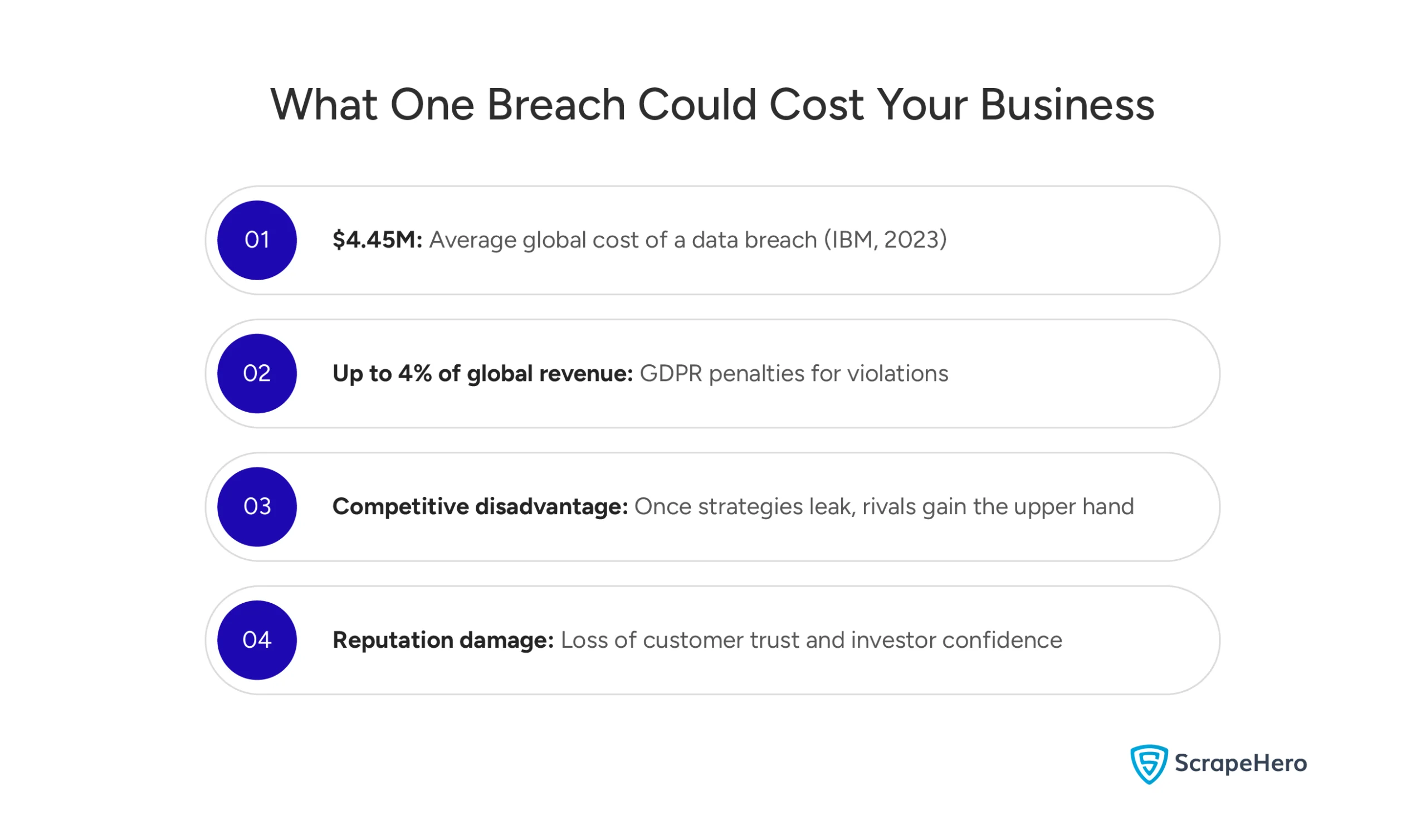
A single data breach from outsourced web scraping can cause serious problems. The average cost of a data breach now exceeds $4.45 million globally. But for businesses, the real damage often comes from:
Regulatory penalties that can reach tens of millions under GDPR or CCPA enforcement. These regulations don’t care if the breach came from internal systems or outside vendors. The responsibility stays with your organization.
Competitive disadvantage when private research methods leak to rivals. Unlike financial losses, competitive intelligence exposure creates permanent market disadvantages.
Reputation damage that hurts customer trust and partner confidence. When businesses fail to protect their data collection processes, people question their ability to safeguard customer information.
Security Risks of Outsourcing Web Scraping
Data Privacy Exposure
The biggest risk isn’t what hackers might steal. Instead, it’s what your vendor’s employees can see about your business operations. Every scraping request reveals something about your strategic priorities and competitive concerns.
Unfortunately, low-quality vendors often give their staff broad access to client data and scraping setups. This means junior developers might have complete access to which competitors you’re watching and what markets you’re considering for expansion.
Even worse, many vendors keep scraped data forever without clear policies about access or storage time. Your competitive intelligence from last quarter might still be accessible to employees who have since moved to other companies – possibly your competitors.
Infrastructure Weaknesses
Most budget web scraping providers use shared infrastructure models that create system-wide security problems:
- Shared proxy networks mean your scraping activities might use the same IP addresses as other clients, creating attribution risks.
- Unencrypted data transfers between scraping nodes expose your data to interception, especially when vendors use overseas teams connected through unsafe networks.
- Poor data separation allows mixing between client datasets, making it impossible to audit who accessed your specific information.
Legal Grey Areas
Understanding the security risks of outsourcing web scraping is crucial because outsourced web scraping operates in a complex legal landscape where responsibility boundaries aren’t clear. While you keep legal responsibility for data protection compliance, you lose direct control over collection methods.
Terms of service violations by your vendor can expose your organization to breach of contract claims and website blocking. This disrupts critical data flows without warning.
Moreover, cross-border data transfers to countries with poor data protection frameworks can violate GDPR requirements, even when the vendor claims compliance.
Legal Risks of Outsourcing Web Scraping
Understanding the Compliance Requirements
Modern businesses operate under increasingly complex data protection frameworks. GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and sector-specific regulations impose strict requirements. These apply whether you handle implementation internally or through vendors.
For example, GDPR compliance requires a clear lawful basis for data processing and appropriate technical measures. When outsourced scraping involves personal data of EU residents, your vendor becomes a data processor under GDPR. This creates joint liability for compliance failures.
Similarly, CCPA requirements mandate transparency about data collection practices. If your scraped data includes personal information of California residents, both you and your vendor must maintain systems capable of responding to consumer requests.
Bypassing Compliance for Speed
The biggest compliance risk comes from vendors who focus on delivery speed over regulatory compliance. These web scraping outsourcing risks become apparent when providers often:
- Skip required legal basis assessments when collecting personally identifiable information.
- Transferring data across borders without adhering to the regulations of the source country
- Fail to implement required technical safeguards.
- Refuse to sign compliant data processing agreements.
International data transfer violations occur when your web scraping vendor handles your data in countries with weaker privacy laws. Here’s how it works: if you’re subject to GDPR (European privacy law) but your vendor processes scraped data in countries that don’t meet GDPR’s protection standards, you’re illegally moving protected data across borders.
Even if you didn’t know where your vendor stores the data, you’re still legally responsible for the violation and can face hefty fines.
Ultimately, a single GDPR violation can result in fines of up to 4% of the company’s global annual revenue. This is a risk that no cost savings can justify.
How to Evaluate Vendor Security?
End-to-End Data Encryption
To ensure security, business-grade vendors must implement complete encryption throughout the entire pipeline:
- Encryption in transit using TLS 1.3 or higher for all data transfers between systems.
- Encryption at rest for all stored data using business-standard algorithms like AES-256.
- Key management systems maintain encryption keys separately from encrypted data, utilizing regular rotation schedules.
Any vendor who can’t provide detailed documentation of their encryption implementation should be immediately disqualified.
Isolated Infrastructure
Shared infrastructure represents an unacceptable risk, so demand that vendors provide:
- Dedicated processing infrastructure where your scraping jobs run on exclusively allocated environments.
- Isolated data storage that physically or logically separates your datasets from other clients’ information.
- Private network configurations that route your data through dedicated paths rather than shared proxy pools.
Clear Data Retention Policies
In addition, business vendors must provide complete transparency about:
- Data retention schedules that specify exactly how long scraped data remains in their systems.
- Storage location documentation identifying specific geographic regions where your data resides.
- Secure deletion procedures with verification that data has been permanently removed from all systems.

Red Flags of Unsafe Outsourced Web Scraping
The “Cheap and Fast” Trick
When vendors offer prices significantly below market rates without explaining their cost structure, they’re almost certainly cutting security corners through:
- Offshore labor arbitrage using developers with minimal cybersecurity training, often working from unsecured networks.
- Shared infrastructure abuse, cramming multiple clients onto common systems to reduce costs.
- Minimal security investment skipping encryption, access controls, and monitoring systems.
The Compliance Avoidance Tactic
The most dangerous red flag involves vendors who actively avoid discussions about legal compliance and regulatory requirements:
- Legal liability deflection through contracts that transfer all responsibility to clients while providing no security assurances.
- Regulatory ignorance is demonstrated by the inability to discuss GDPR, CCPA, or industry-specific compliance requirements.
- Documentation resistance, characterized by a refusal to provide security policies or audit reports that legitimate vendors readily share.
How a Secure Outsourced Web Scraping Service Should Work
The Complete Security Workflow

In contrast, business-grade secure outsourced web scraping follows a structured process:
Phase 1: Secure Requirements Gathering begins with complete NDAs and security assessments that identify data sensitivity levels and regulatory requirements.
Phase 2: Infrastructure Setup involves setting up dedicated environments with client-specific encryption keys and documented security controls.
Phase 3: Compliant Data Collection uses legally vetted methods that respect websites’ terms of service and maintain detailed audit trails.
Phase 4: Secure Data Processing applies encryption and access controls throughout the pipeline, ensuring data never exists in vulnerable states.
Phase 5: Protected Delivery transfers completed datasets through encrypted channels with verification and immediate vendor-side deletion.
Phase 6: Ongoing Security Monitoring provides continuous surveillance with regular reporting and immediate incident response capabilities.
The RPA Security Multiplier
Additionally, a good web scraping vendor will use Robotic Process Automation (RPA) that reduces human handling while improving security:
- Automated data handling eliminates manual intervention points where human error could compromise security.
- Consistent security policy enforcement through programmatic controls, ensuring every dataset receives identical protection measures.
- Enhanced audit capabilities through complete automation logging for regulatory compliance and security investigations.
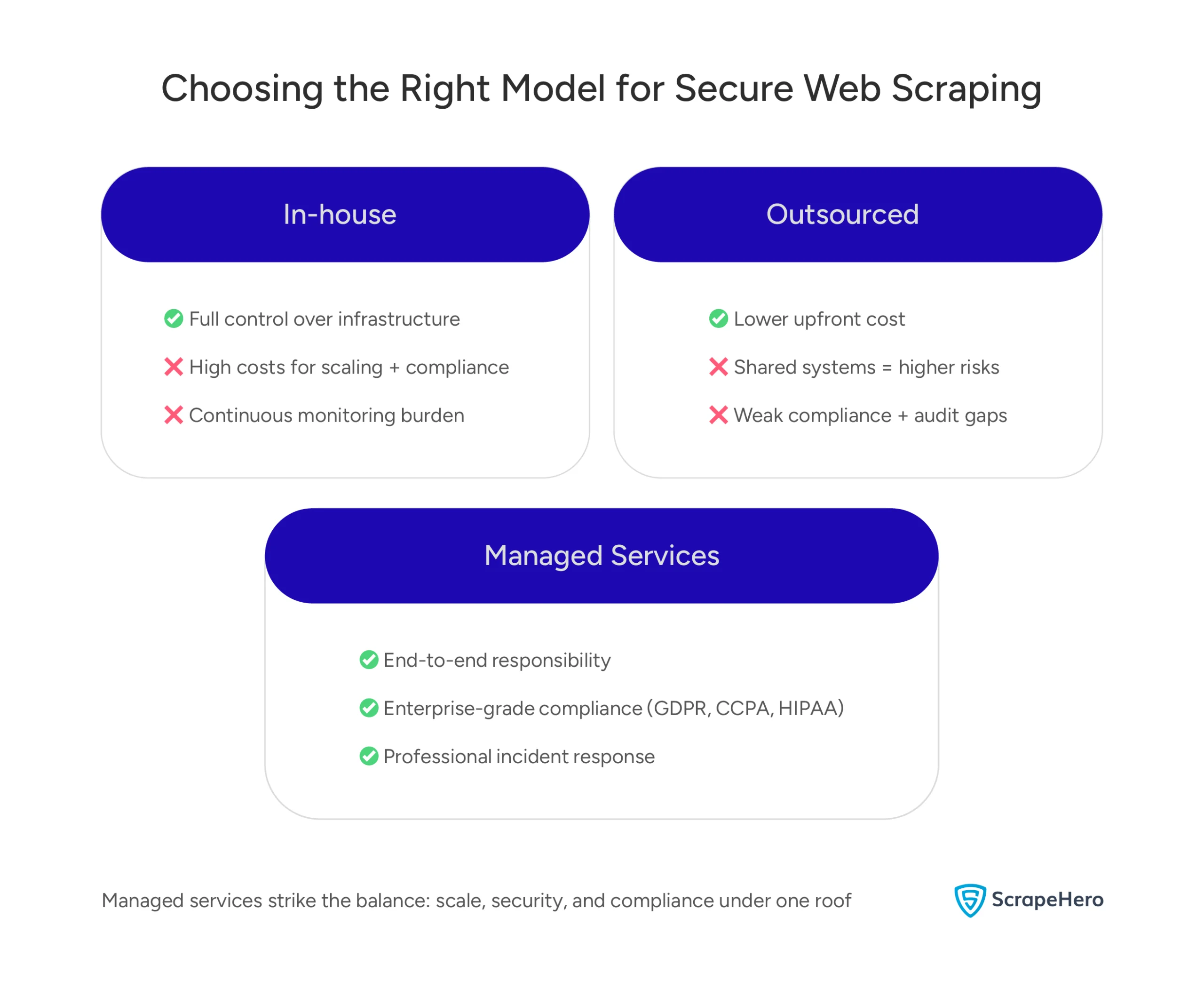
Why Managed Services Beat Outsourcing Individual Tasks
The Freelancer Security Problem
Individual freelancers and small agencies create security exposures that no business should accept:
- No security infrastructure means data gets processed on personal computers using consumer-grade tools without encryption.
- Zero regulatory compliance because contractors lack the legal infrastructure necessary for business data protection requirements.
- No incident response capabilities, leaving you completely exposed if security breaches occur.
The Managed Service Security Advantage
In contrast, completely managed services provide integrated security:
- End-to-end responsibility where a single vendor maintains accountability across the entire data pipeline.
- Integrated compliance management combining legal assessment, technical implementation, and ongoing monitoring.
- Professional incident response with dedicated security teams and established procedures.
ScrapeHero’s Approach to Outsourced Web Scraping Security
ScrapeHero’s web scraping service provides a secure, business-grade data platform. We engineer security and compliance into our operations, ensuring enterprises receive trusted, reliable data from start to finish.
Business-Grade Security Architecture
- Dedicated infrastructure environments ensure complete client isolation with no shared resources.
- Military-grade encryption protects all data during transfers.
- Zero-trust access controls implement granular permissions with complete audit trails for regulatory compliance.
Compliance-First Method
- Proactive legal assessment evaluates every project against applicable regulations before collection begins.
- Complete data processing agreements clearly define responsibilities under GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations.
- Regular audits to ensure our security controls and compliance procedures.
Proven Business Trust
- Fortune 500 clients rely on our security capabilities for their most sensitive competitive intelligence needs.
- Zero security incidents across our entire operational history reflect our commitment to protective measures.
Ready to transform public web data into a strategic asset, confidently and without compromise?
Our fully managed data pipelines ensure your sensitive business intelligence remains protected while delivering the competitive insights you need to succeed.
Contact ScrapeHero today to discuss how our secure outsourced web scraping approach can support your data collection needs without compromising your organization’s risk profile.
FAQ
The biggest risks come from poor execution. If scraping is done without proper security, it can expose sensitive business data, cause IP bans, or even lead to data breaches. Legally, scraping that violates a site’s terms of service or uses unapproved methods can trigger lawsuits. Reputation damage is another risk if customers or partners see scraping tied to unethical practices; trust erodes quickly.
Scraping isn’t outright illegal in the US. Courts have ruled that collecting publicly available data can be lawful (hiQ v. LinkedIn being a key case). But scraping private data, bypassing security controls, or ignoring intellectual property rights can cross into illegal territory. It’s legal when done responsibly, with compliance and ethics in mind.
Yes. Websites track visitor activity through server logs, IP addresses, and user-agent strings. If scraping is done carelessly using the same IP, making too many requests, or ignoring robots.txt, it can be detected quickly. Secure, business-grade scraping uses proxy rotation, request throttling, and ethical practices to reduce traceability while staying compliant.
It can be, but only if handled correctly. GDPR applies when scraping involves personal data of EU residents. To be compliant, companies must ensure there’s a lawful basis for processing, respect data minimization principles, and secure the data during transfer and storage. Outsourced scraping vendors should act as processors under a clear Data Processing Agreement (DPA). Without these measures, scraping personal data risks GDPR violations.








