This tutorial walks you through two ways to scrape data from Target.com: one with no coding needed and another for those who like to write code. First up, we have the no-code method using ScrapeHero Cloud’s Target Product and Pricing scraper. It’s an easy method to scrape Target without coding—just a few clicks and you can grab all the product details you need!
Next, the tutorial also covers using Python Playwright for Target data extraction. This method lets you search for and extract product info in a straightforward way.
Let’s start!
With ScrapeHero Cloud, you can download data in just two clicks!Don’t want to code? ScrapeHero Cloud is exactly what you need.
How Do You Scrape Target.com Without Coding?
You can effortlessly extract data from Target.com using ScrapeHero Cloud’s Target Product Data and Pricing Scraper, no coding skills required!
The scraper can extract product data using any of the following inputs:
- Category or Search URL
- Product Name
- GTIN (Global Trade Item Number)
- ISBN (International Standard Book Number)
- UPC (Universal Product Code)
- Part Number
- Keyword
Follow these steps to start scraping Target.com for free:
1. Log In to ScrapeHero Cloud
First, log in to your ScrapeHero Cloud account. If you’re new to the platform, creating an account is simple and only takes a few minutes.

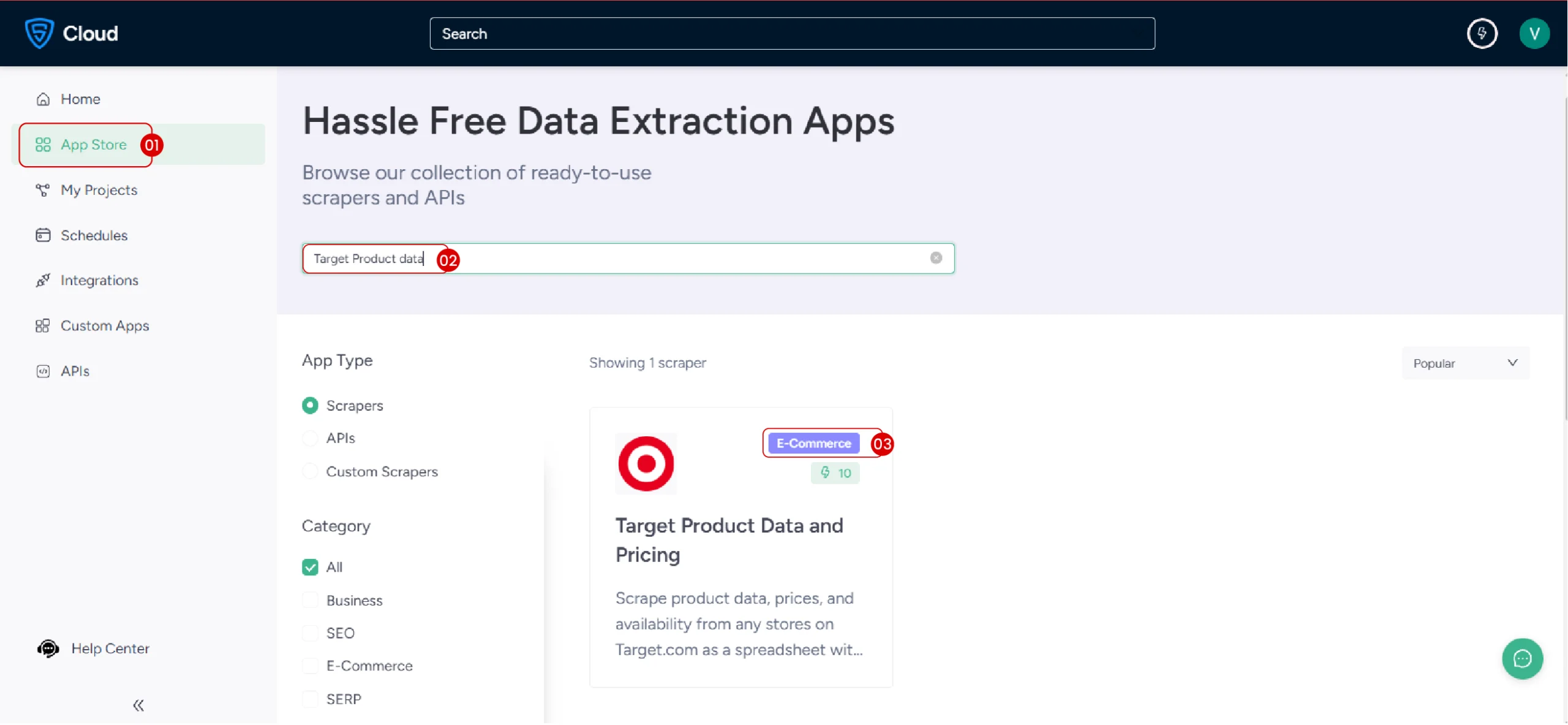
2. Find the Target Scraper
Once logged in, navigate to the ScrapeHero App Store and locate the Target Product Data and Pricing scraper.
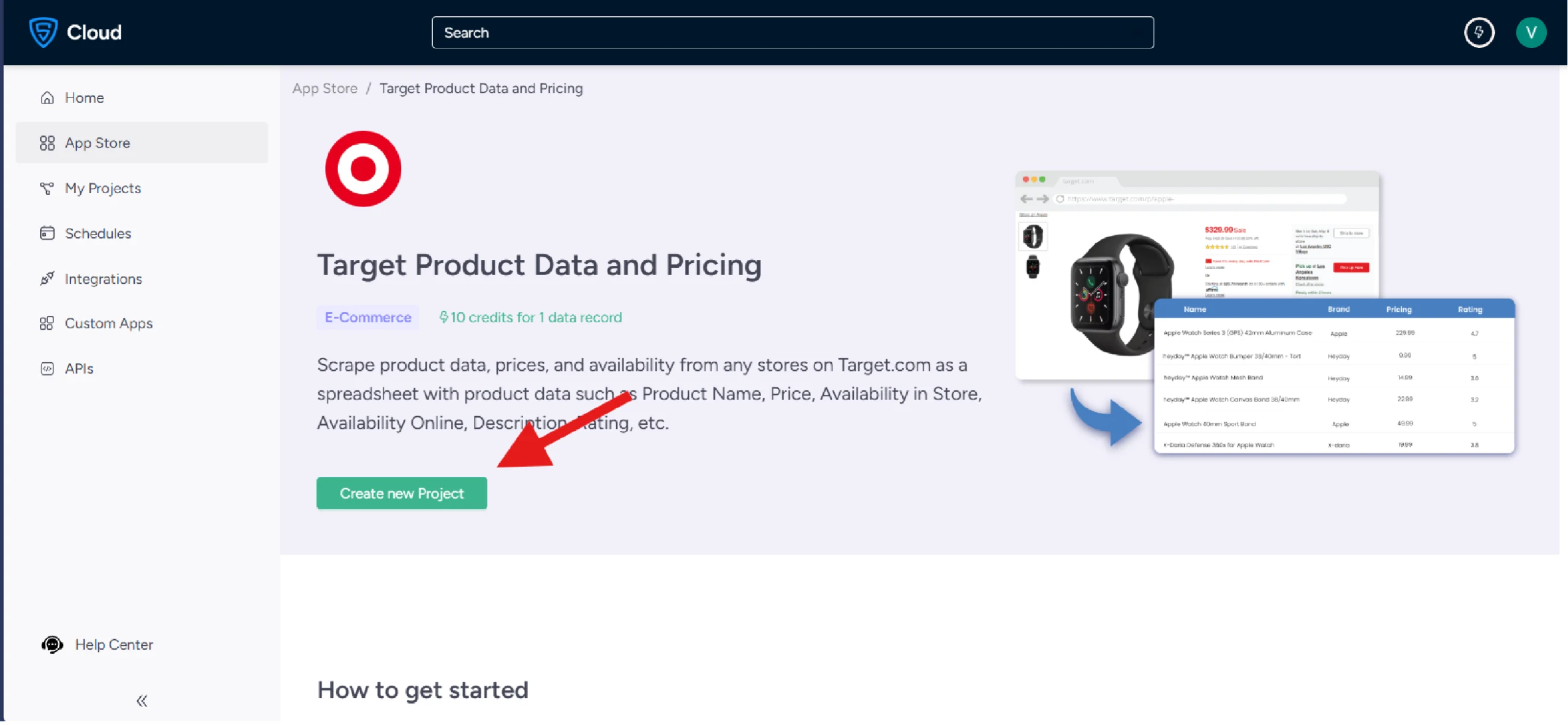
 3. Create Your Project
3. Create Your Project
Select the scraper and start your project by clicking the “Create New Project” button. You are now ready to gather data from the products that interest you!
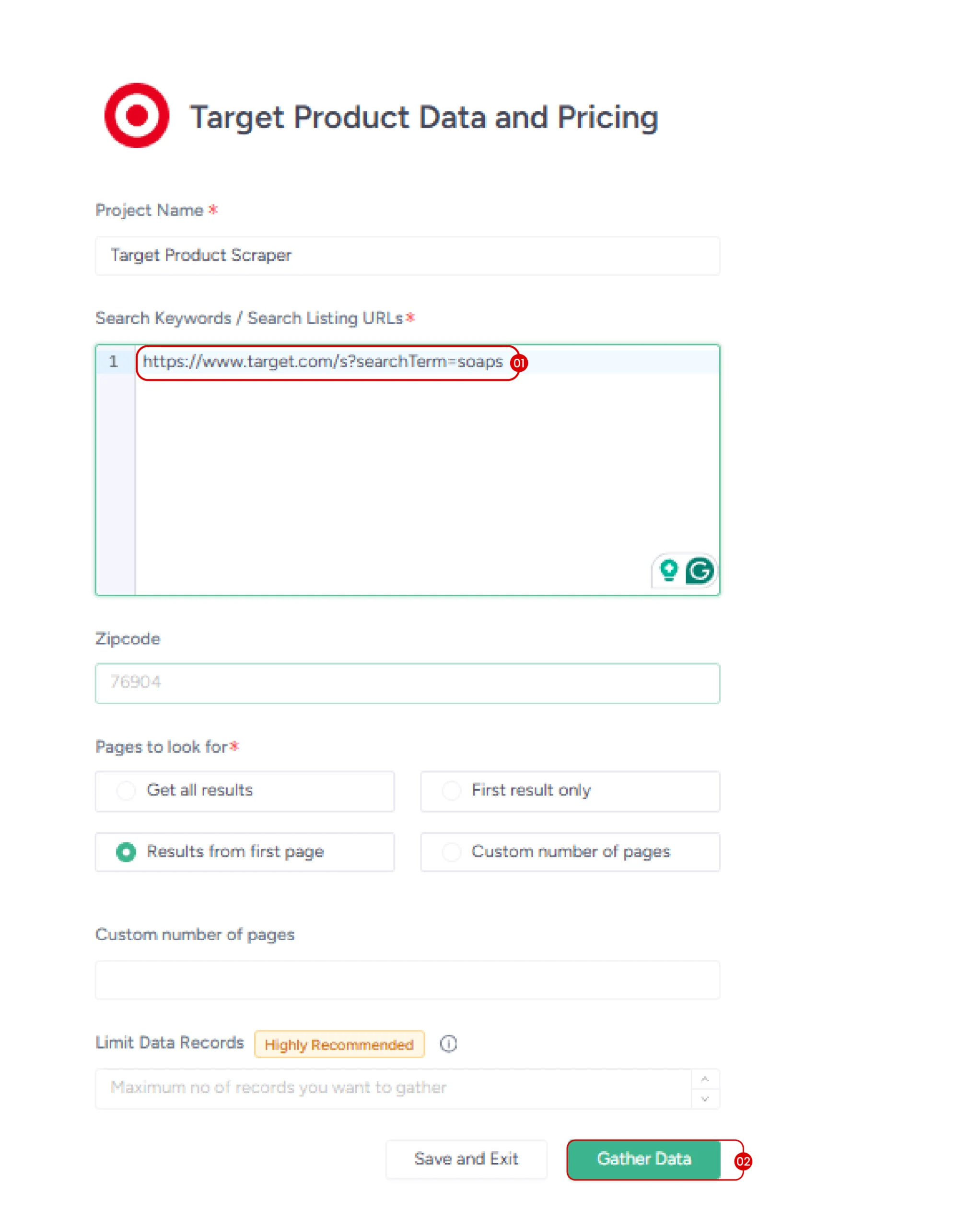
 4. Gather the inputs
4. Gather the inputs
Search for the product you want to scrape on Target.com. Copy the search URL to extract data from the products listed. If you have specific products in mind, gather their identifying details, such as product name, GTIN, ISBN, etc
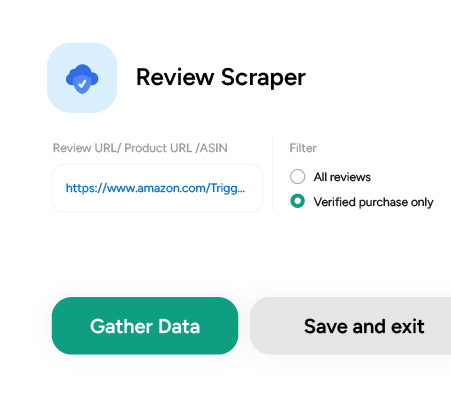
 5. Begin Data Extraction
5. Begin Data Extraction
Paste your chosen input (for example, search URL) and click ‘Gather Data’. The scraper will then extract key details, including product title, price, customer ratings, reviews, and availability.
6. Download Your Data
Once the scraping process is complete, you can download the gathered data in formats like CSV, JSON, or Excel.
This no-code approach allows you to extract information quickly. Additionally, ScrapeHero Cloud offers advanced features such as automatic scheduling, direct data uploads to cloud storage, and API integration to help you scale your workflow effectively.
Scraping Target.com With Python
If you’d rather code your own scraper, here’s how you can build one with Python and Playwright. This script will search Target.com for a product and pull the first 10 results.
What Do You Need to Scrape Target?
The code shown in this article only needs Playwright for data extraction. You can use pip to install Playwright.
pip install Playwright
After installing the Playwright library, you also need to install the Playwright browser.
playwright install
You can now import sync_playwright from playwright.sync_api.
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwright
import json
The above code also imports the json module to save the extracted data.
After importing the necessary packages, launch the Playwright browser and navigate to “Target.com.”
with sync_playwright() as p:
context = p.chromium.launch()
page = context.new_page()
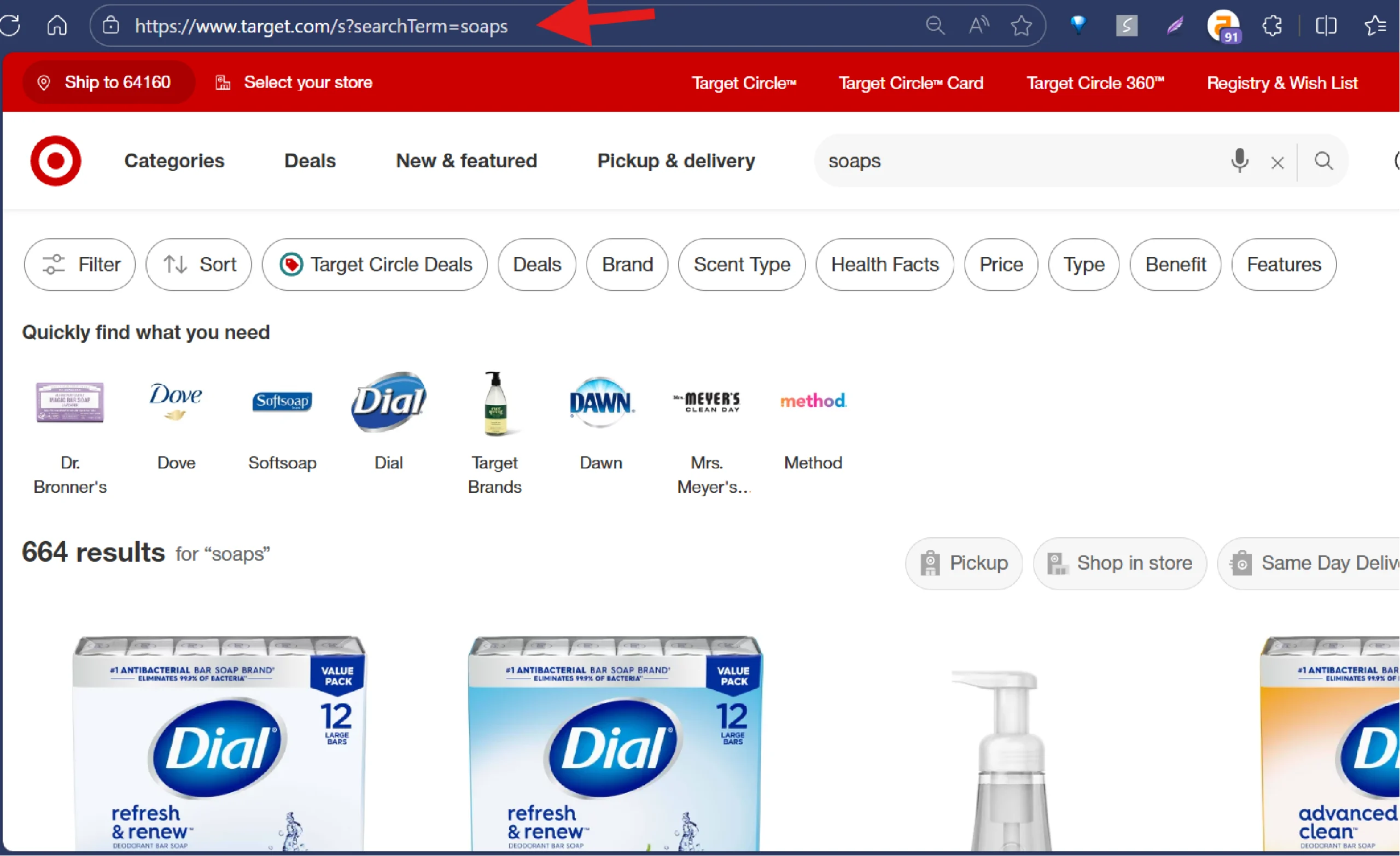
page.goto("https://www.target.com/")Next, you need to search for a product.
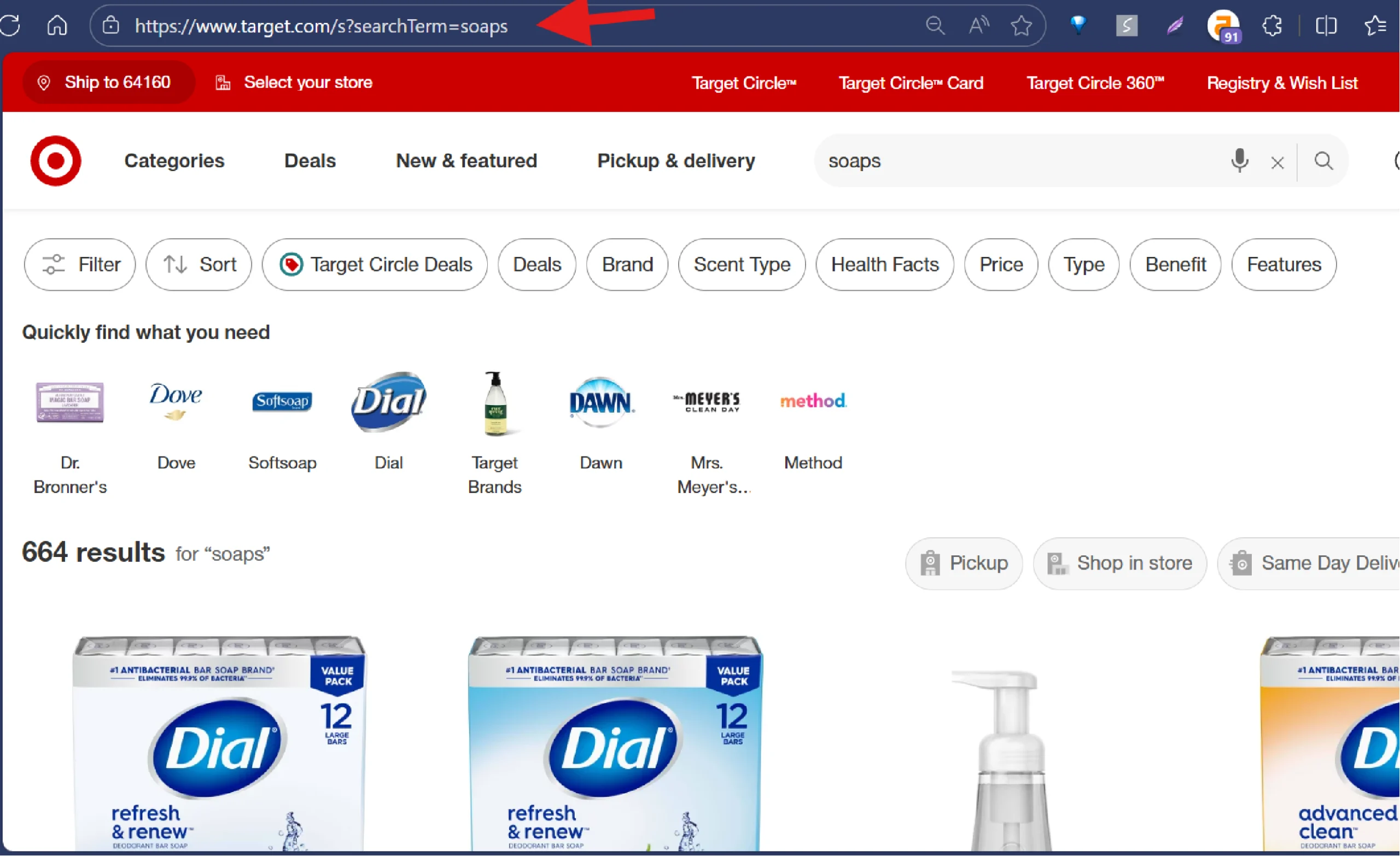
How Do You Search for Products on Target using Playwright?
To search for products on Target with Playwright, you must inspect the search box by right-clicking on it and selecting “Inspect.” This will reveal that the search box is an input element with “searchTerm” as its name attribute.
You can then use
- The query_selector() method to select the search box
- The fill() method to enter the search term
- The press() method to press the Enter key
product = "soaps"
page.wait_for_selector('input[name="searchTerm"]')
search_input = page.query_selector('input[name="searchTerm"]')
search_input.fill(product)
search_input.press('Enter')Note: The code uses the wait_for_selector() method to ensure that the element has fully loaded.
Pressing ‘Enter’ loads a list of product cards from which you can extract product details.
How Do You Collect Target Product Cards?
To collect Target product cards, you need to determine their unique selector first.
Inspecting the product card shows that it is a div element with the class “product_card.” Select them using query_selector_all().
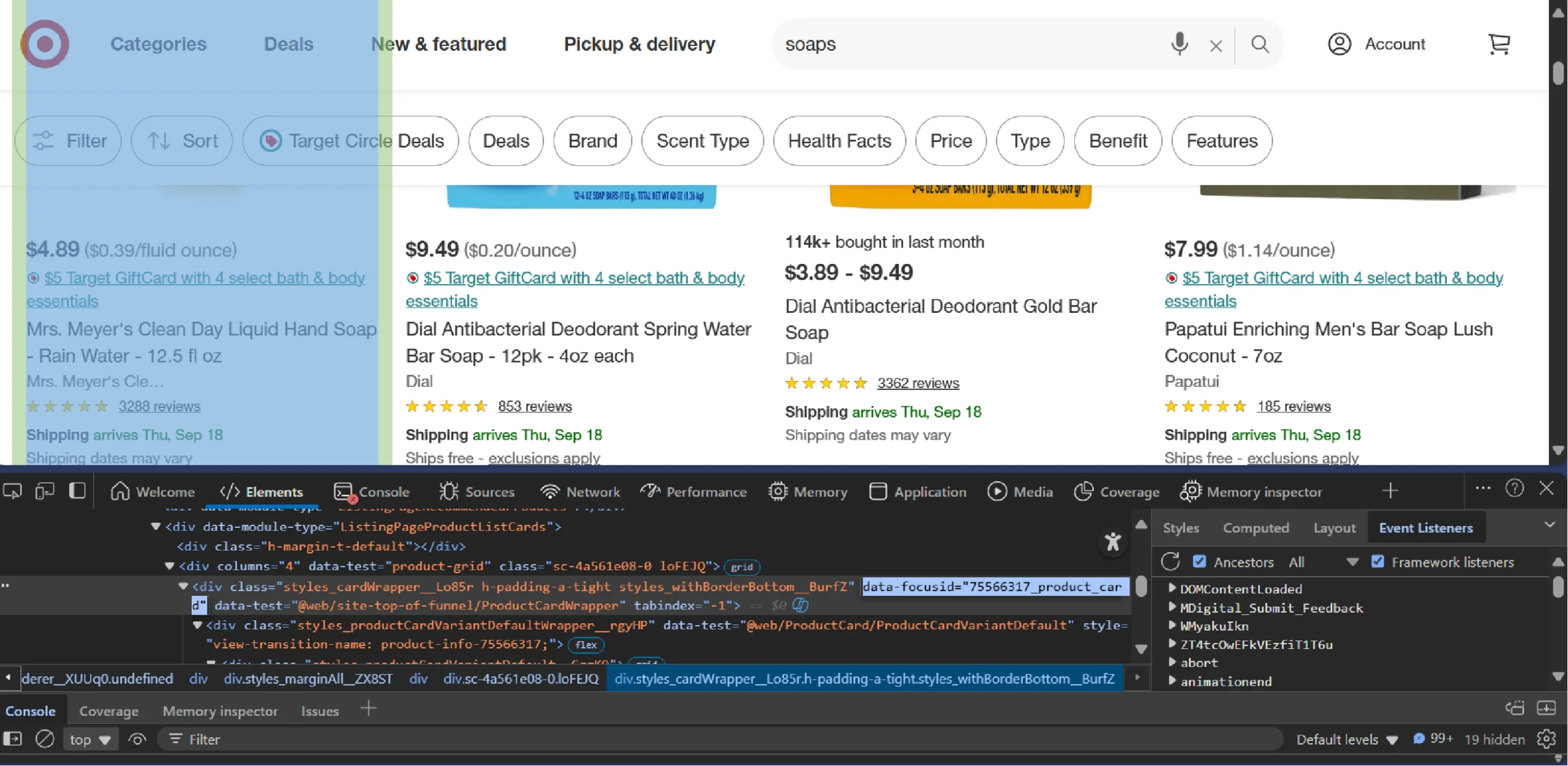
page.wait_for_selector('div[data-focusid*="product_card"]')
product_cards = page.query_selector_all('div[data-focusid*="product_card"]')Now, you’ve got a list of product cards to loop through and extract details.
How Do You Extract Details from Target’s Product Cards?
Extracting details from product cards requires you to
- Inspect each data point, such as price, rating, etc.
- Determine the CSS selectors for each
- Extract the data points using the selectors
product_details = []
for card in product_cards[:10]:
price = card.query_selector('span[data-test="current-price"] > span').text_content()
anchor_tag = card.query_selector('a')
relative_url = anchor_tag.get_attribute('href').split('?')[0]
url = "https://target.com" + relative_url
title = relative_url.split('/')[2].replace('-', ' ').title()
rating_element = card.query_selector('span[data-test="ratings"] > span')
rating_text = rating_element.text_content().split() if rating_element else None
if rating_text:
rating = rating_text[0]
rating_count = rating_text[-2]
else:
rating, rating_count = "NA", "NA"
product_details.append({
'title': title,
'price': price,
'rating': rating,
'rating_count': rating_count,
'url': url,
})
The code uses the query_selector() method to extract the following:
- The price from a span element
- The title and URL from an anchor tag
- The rating details from a span element
How Do You Save Your Results after Scraping?
Once you’ve collected products, save them as JSON so you can analyze them later. Use json.dump() to do so.
if __name__ == "__main__":
products = scrape_target_products()
with open("target_products.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(products, f, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)
print("Saved target_products.json")
This code saves the data in a file “target_products.json” in prett-printed format, which will look like this:
{
"title": "Method Gel Hand Soap",
"price": "$3.99",
"rating": "4.6",
"rating_count": "254",
"url": "https://target.com/p/method-gel-hand-soap"
}
Are There Any Limitations to This Scraping Code?
Although you can scrape data from Target.com, there are several limitations:
- The CSS selectors used in this code rely on HTML structure, which means they may break if the structure changes
- The code doesn’t include techniques to handle anti-scraping measures, making it unsuitable for large-scale operations
- Headless browsers are resource intensive, making them highly sensitive to network issues
Why a Web Scraping Service Might be a Better Option?
The no-code option outlined in this tutorial works well for small-scale web scraping but has its limitations when it comes to larger projects. Plus, you’ll need to handle the code yourself, which can make things more complicated.
On the other hand, the no-code Scraper allows users to tackle larger scraping tasks with ease, making it accessible even if you don’t have any programming skills.
If you’re serious about scraping data on a larger scale with customized data points, ScrapeHero’s top-notch web scraping service is the way to go.
As one of the leading web scraping service providers around the globe, ScrapeHero specializes in building enterprise-grade scrapers and crawlers tailored to your specific needs. Team up with ScrapeHero today, and let us simplify data extraction for you, so you can focus on driving your business forward.








